Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Complete the following diagrams shown in the following figures by drawing the reflected rays.
उत्तर
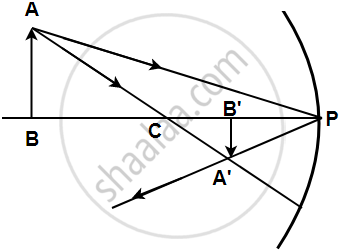
A light ray coming from a point on object AB is reflected from the surface of the mirror, it passes through the principal focus and the other ray passing through the center of curvature strikes the mirror normally i.e. 90 degrees. Hence it will reflect back. These two reflected rays coincide at a point where the image is formed. The image, A'B' is real, inverted, and diminished in size.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define the following term in the context of spherical mirrors:- Centre of curvature
What is the relation between the focal length and radius of curvature of a spherical mirror (concave mirror of convex mirror)? Calculate the focal length of a spherical mirror whose radius of curvature is 25 cm.
When a spherical mirror is held towards the sun and its sharp image is formed on a piece of a carbon paper for some time, a hole is burnt in the carbon paper.
What is the nature of spherical mirror?
Upto what maximum distance from a concave mirror, the image can be obtained? What will be the location of object for it?
The magnification for a mirror is -3. How are u and v related?
The image formed by a convex mirror is of size one third the size of object. How are u and v related?
Answer the following question:
Distinguish between the convex mirror and the concave mirror.
Define the term principal focus in case of convex mirror. Draw a convex mirror and show its principal focus and focal length clearly.
