Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer the following question:
Distinguish between the convex mirror and the concave mirror.
उत्तर
Convex mirror and concave mirror.
| Convex mirror | Concave mirror | |
| 1. | It is called a diverging mirror. | It is called a converging mirror. |
| 2. | The light is reflected from the outer surface. | The light is reflected from the inner surface. |
| 3. | It can form only a virtual image | It can form a real image as well as a virtual image. |
| 4. | According to sign convention, the focal length is positive. | According to sign convention, the focal length is negative. |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A 4 cm tall object is placed on the principal axis of a convex lens. The distance of the object from the optical centre of the lens is 12 cm and its sharp image is formed at a distance of 24 cm from it on a screen on the other side of the lens. If the object is now moved a little away from the lens, in which way (towards the lens or away from the lens) will he have to move the screen to get a sharp image of the object on it again? How will the magnification of the image be affected?
Define the following term in the context of spherical mirrors:- Principal axis
Explain the following term related to spherical lenses:- principal axis
Explain the following term related to spherical lenses: focal length
An image formed by a ______ mirror is always of the same size as that of the object.
What happens when a ray of light falls normally (or perpendiculary) on the surface of a plane mirror?
A ray of light is incident normally on a plane mirror. What will be the
angle of reflection?
What is the relation between the focal length and radius of curvature of a spherical mirror (concave mirror of convex mirror)? Calculate the focal length of a spherical mirror whose radius of curvature is 25 cm.
Write the formula for a lens connecting image distance (v), object distance (u) and the focal length (f). How does the lens formula differ from the mirror formula?
How is a spherical mirror used to diverge a beam of light from a point? Name the type of mirror used.
State the direction of incident ray which after reflection from a spherical mirror gets reflected along its own path. Give a reason.
An optical device has been given to a student and he determines its focal length by focusing the image of the sun on a screen placed 24 cm from the device on the same side as the sun. Select the correct statement about the device.
(A) Convex mirror of focal length 12 cm
(B) Convex lens of focal length 24 cm
(C) Concave mirror of focal length 24 cm
(D) Convex lens of focal length 12 cm
Complete the following diagrams in Figure by drawing the reflected rays for the incident rays 1 and 2.
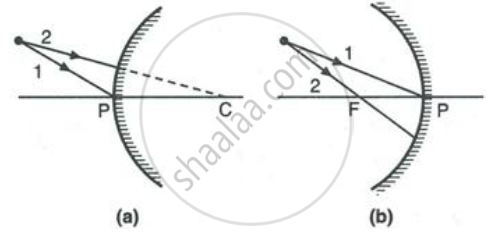
State the two convenient rays that are chosen to construct the image by a spherical mirror for a given object? Explain your answer with the help of suitable ray diagrams.
For what position of object, the image formed by a concave mirror is magnified and erect?
State whether the image in part (a) is real or virtual?
State the position of object for which the image formed by a concave mirror is of same size.
Does the mirror mentioned in part (b) form real image for all locations of the object?
Name the kind of mirror used to obtain:
A virtual and enlarged image
Name the kind of mirror used to obtain:
A real and diminished image.
State the kind of mirror used
(a) By a dentist,
(b) As a search-light reflector.
The focal length of a concave mirror is 10 cm. Find its radius of curvature.
The magnification for a mirror is -3. How are u and v related?
Answer the following question.
Write the modification in the curvature of the eye lens which enables us to see the nearby objects clearly?
Select the correct option:
Looking into a mirror one finds her image diminished, the mirror is:
Define the following term in relation to concave mirror.
Center of curvature
What is the relation between focal length and radius of curvature of a concave mirror?
Define the term Principal axis.
Define linear magnification produced by a mirror?
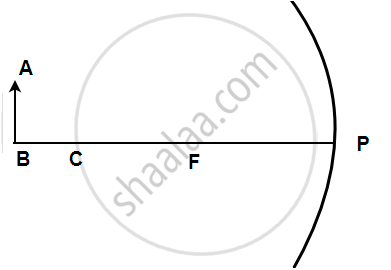
The following figure shows a concave mirror with its pole (P), focus (F), and center of curvature (C). Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image of an object AB by the concave mirror.
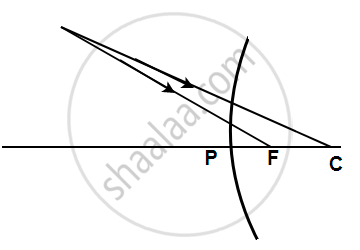
Complete the following diagrams shown in the below figure by drawing the reflected ray for each incident ray.
An object 10 cm high is placed at a distance of 20 cm in front of a spherical mirror of focal length 25 cm. By scale drawing find the nature, position, and magnification of the image in the following case:
Concave mirror
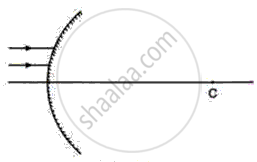
The diagram below shows the parallel rays incident on a convex mirror. C is the centre of the curvature of the mirror. By drawing the paths of the reflected rays, label the focus F and hence find the focal length of the mirror.
The spherical mirror with a reflecting surface curved inward is called
The distance from the pole to the focus is called ______.
Numerical problem.
The radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is 25 cm. Find its focal length.
Name the type of mirror used in the following situation:
Side/rear-view mirror of a vehicle
Support your answer with reason.
The radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is 18 cm. What is the focal length of this mirror?
How tall does a mirror have to be to fit an entire person’s body?
