Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The following figure shows a concave mirror with its pole (P), focus (F), and center of curvature (C). Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image of an object AB by the concave mirror.
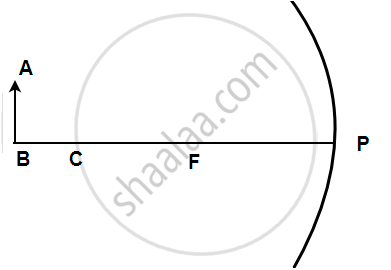
उत्तर

A light ray, parallel to the principal axis, coming from a point on object AB is reflected from the surface of the mirror, it passes through the principal focus and the other ray passing through the center of curvature strikes the mirror normally i.e. 90 degrees. Hence it will reflect back. These two reflected rays coincide at a point between F and C, where the image is formed. The image, A'B' is real, inverted, and diminished in size.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A ray of light travels from a denser medium to a rarer medium. How will it bend?
What do you mean by the term dispersion?
State the direction of incident ray which after reflection from a spherical mirror gets reflected along its own path. Give a reason.
Figure shows a concave mirror with its pole at P, focus F and centre of curvature C. Draw ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object OA.
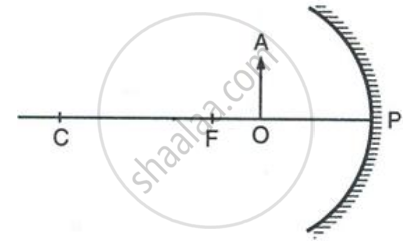
State the position of object for which the image formed by a concave mirror is of same size.
Does the mirror mentioned in part (b) form real image for all locations of the object?
Define the term principal focus in case of convex mirror. Draw a convex mirror and show its principal focus and focal length clearly.
Name the type of mirror used in the following situation:
Side/rear-view mirror of a vehicle
Support your answer with reason.
Name the type of mirror used in the following situation:
Solar furnace
Support your answer with reason.
The radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is 18 cm. What is the focal length of this mirror?
