Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The following figure shows a concave mirror with its pole (P), focus (F), and center of curvature (C). Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image of an object AB by the concave mirror.
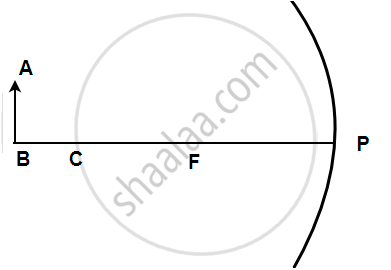
Solution

A light ray, parallel to the principal axis, coming from a point on object AB is reflected from the surface of the mirror, it passes through the principal focus and the other ray passing through the center of curvature strikes the mirror normally i.e. 90 degrees. Hence it will reflect back. These two reflected rays coincide at a point between F and C, where the image is formed. The image, A'B' is real, inverted, and diminished in size.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Image formed by a convex ______ is always virtual and smaller in size.
Match the items given in Column I with one or more items of Column II.
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (a) | A plane mirror | (i) | Used as a magnifying glass. |
| (b) | A convex mirror | (ii) | Can form image of objects spread over a large area. |
| (c) | A convex lens | (iii) | Used by dentists to see enlarged image of teeth. |
| (d) | A concave mirror | (iv) | The image is always inverted and magnified. |
| (e) | A concave lens | (v) | The image is erect and of the same size as the object. |
| (vi) | The image is erect and smaller in size than the object. |
What is the relation between the focal length and radius of curvature of a spherical mirror (concave mirror of convex mirror)? Calculate the focal length of a spherical mirror whose radius of curvature is 25 cm.
AB and CD, two spherical mirrors, from parts of a hollow spherical ball with its centre at O as shown in the diagram. If arc AB = `1/2` arc CD, what is the ratio of their focal lengths? State which of the two mirrors will always form virtual image of an object placed in front of it and why.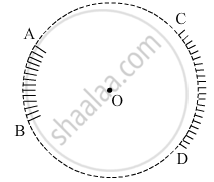
State the types of mirrors used for (i) headlights and (ii) rear view mirror, in cars and motorcycles. Give to justify your answer in each case.
Complete the following diagrams in Figure by drawing the reflected rays for the incident rays 1 and 2.
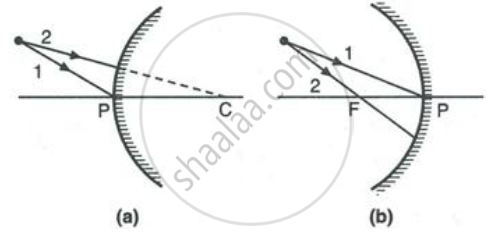
Answer the following question.
Write the modification in the curvature of the eye lens which enables us to see the nearby objects clearly?
Define the following term:
spherical mirror
