Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The following figure shows a concave mirror with its pole (P), focus (F), and center of curvature (C). Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image of an object AB by the concave mirror.
उत्तर

A light ray, parallel to the principal axis, coming from a point on object AB is reflected from the surface of the mirror, it passes through the principal focus and the other ray passing through the center of curvature strikes the mirror normally i.e. 90 degrees. Hence it will reflect back. These two reflected rays coincide at a point between F and C, where the image is formed. The image, A'B' is real, inverted, and diminished in size.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Give one use each of a concave and a convex mirror.
Name the two types of spherical mirrors. What type of mirror is represented by the:
front side of a shining steel spoon?
Name the spherical mirror which can produce a virtual and diminished image of an object.
Name the kind of mirror used to obtain:
A virtual and diminished image
Select the correct option:
Looking into a mirror one finds her image diminished, the mirror is:
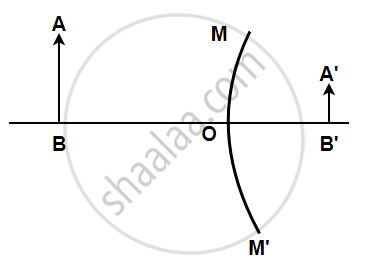
AB is the object, A1B1 is its image. MM' is the position of the mirror. Complete the ray diagram and find the position of the center of curvature and focus of the mirror. Also, measure the focal length.
Numerical problem.
The radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is 25 cm. Find its focal length.
The minimum length of the mirror required to see the full image of the person is half ‘ of his height.
