Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
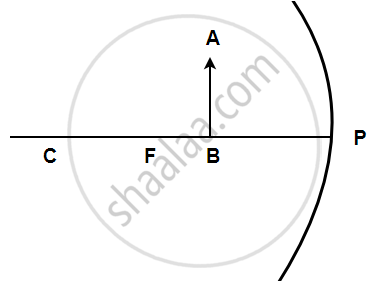
In the following figure shows a concave mirror with its pole (P), focus (F) and centre of curvature (C). Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image of an object AB by the concave mirror.
उत्तर
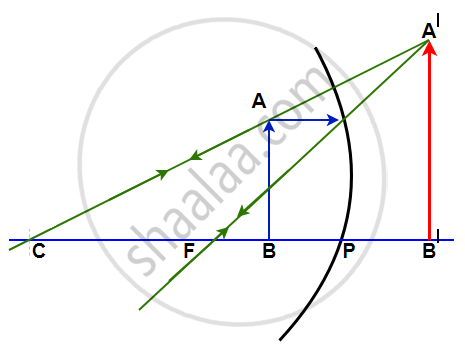
A light ray, parallel to the principal axis, coming from a point on object AB is reflected from the surface of the mirror, it passes through the principal focus and the other ray striking normally to the mirror reflects back and passes through the center of curvature. These two reflected rays, when produced backward, coincide at a point where the image is formed. The image, A'B' is virtual, erect, and magnified in size.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A concave mirror always forms a real image.
Which are the two convenient rays that are chosen to construct the image by a spherical mirror for a given object? Explain with the help of suitable ray diagrams.
Draw suitable diagrams to illustrate the action of (i) concave mirror and (ii) convex mirror on a beam of light incident parallel to the principal axis.
An object 5 cm high is placed at a distance 60 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm. Find the position and size of the image.
Define the following term in relation to concave mirror.
Principal focus
The spherical mirror with a reflecting surface curved inward is called
In torches, search lights and headlights of vehicles the bulb is placed ______.
What is the focal length (f) of a mirror?
In the figure shown, the image of a real object is formed at the point I. AB is the principal axis of the mirror. The mirror must be: