Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In the following figure shows a concave mirror with its pole (P), focus (F) and centre of curvature (C). Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image of an object AB by the concave mirror.
उत्तर
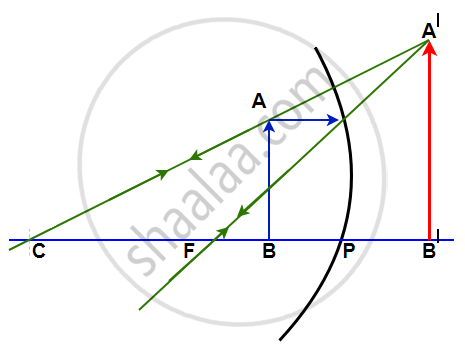
A light ray, parallel to the principal axis, coming from a point on object AB is reflected from the surface of the mirror, it passes through the principal focus and the other ray striking normally to the mirror reflects back and passes through the center of curvature. These two reflected rays, when produced backward, coincide at a point where the image is formed. The image, A'B' is virtual, erect, and magnified in size.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A student focused the Sun rays using an optical device 'X' on a screen S as shown.

From this it may be concluded that the device 'X' is a (select the correct option)
(A) Convex lens of focal length 10 cm.
(B) Convex lens of radius of curvature 20 cm.
(C) Convex lens of focal length 20 cm.
(D) Concave mirror of focal length 20 cm.
Match the items given in Column I with one or more items of Column II.
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (a) | A plane mirror | (i) | Used as a magnifying glass. |
| (b) | A convex mirror | (ii) | Can form image of objects spread over a large area. |
| (c) | A convex lens | (iii) | Used by dentists to see enlarged image of teeth. |
| (d) | A concave mirror | (iv) | The image is always inverted and magnified. |
| (e) | A concave lens | (v) | The image is erect and of the same size as the object. |
| (vi) | The image is erect and smaller in size than the object. |
Name the two types of spherical mirrors. What type of mirror is represented by the:
back side of a shining steel spoon?
A ray of light travels from a denser medium to a rarer medium. How will it bend?
State the types of mirrors used for (i) headlights and (ii) rear view mirror, in cars and motorcycles. Give to justify your answer in each case.
For an incident ray directed towards centre of curvature of a spherical mirror the reflected ray:
Define the following term:
convex mirror
The radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is 18 cm. What is the focal length of this mirror?
