Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
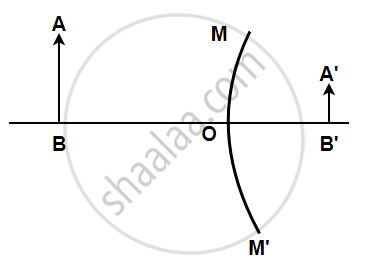
AB is the object, A1B1 is its image. MM' is the position of the mirror. Complete the ray diagram and find the position of the center of curvature and focus of the mirror. Also, measure the focal length.
उत्तर
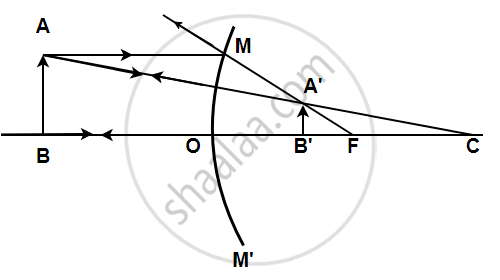
A light ray coming from a point on object AB is reflected from the surface of the mirror. When this ray is produced backwards, it passes through the principal focus and the ray which traces its incident path after reflection, when produced backwards, passes through the centre of curvature. These two reflected rays coincide at a point where the image is formed. The image, A'B' is virtual, erect, and diminished in size The focal length was found to be 24 mm.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define (a) centre of curvature (b) radius of curvature (c) pole (d) principal axis, and (e) aperture, of a spherical mirror with the help of a labelled diagram
State the direction of incident ray which after reflection from a spherical mirror gets reflected along its own path. Give a reason.
Name the kind of mirror used to obtain :
A real and enlarged image
How is the focal length of a spherical mirror related to its radius of curvature?
Answer the following question.
Write the modification in the curvature of the eye lens which enables us to see the nearby objects clearly?
Define linear magnification produced by a mirror?
The boxes in figure (a, b, c) represent mirrors; insert a mirror which will reflect the incident ray as shown in the diagram.
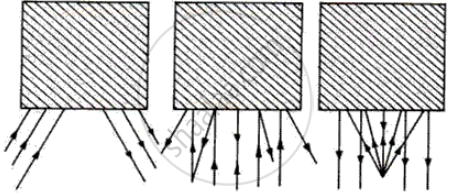
Complete the following diagrams shown in the following figures by drawing the reflected rays.

The spherical mirror used as a rear view mirror in the vehicle is
