Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
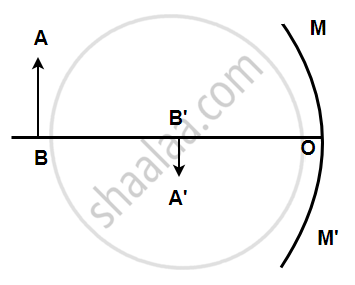
AB is the object, A'B' is the image, and MM' is the position of the mirror. Complete the ray diagram showing the formation of the image and find the focal length of the mirror.
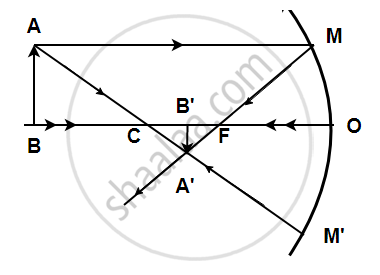
उत्तर
A light ray coming from a point on object AB is reflected from the surface of the mirror, it passes through the principal focus and the other ray passing through the center of curvature strikes the mirror normally i.e. 90 degrees. Hence it will reflect back. These two reflected rays coincide at a point where the image is formed. The image, A'B' is real, inverted, and diminished in size. The focal length was found to be 16 mm.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name the spherical mirror which has:
(a) virtual principal focus.
(b) real principal focus.
When a spherical mirror is held towards the sun and its sharp image is formed on a piece of a carbon paper for some time, a hole is burnt in the carbon paper.
What name is given to the distance between spherical mirror and carbon paper?
A lens forms a real image 3 cm high of an object 1 cm high. If the separation of object and image is 15 cm, find the focal length of the lens.
A diverging lens is used in:
(a) a magnifying glass
(b) a car to see objects on rear side
(c) spectacles for the correction of short sight
(d) a simple camera
A 50 cm tall object is at a very large distance from a diverging lens. A virtual, erect and diminished image of the object is formed at a distance of 20 cm in front of the lens. How much is the focal length of the lens?
Complete the following diagrams shown in Fig. by drawing the reflected ray for each of the incident ray A and B.
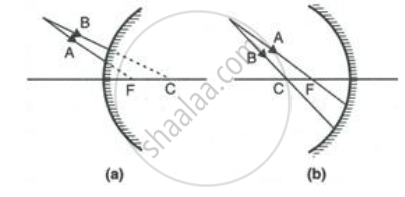
For an incident ray directed towards centre of curvature of a spherical mirror the reflected ray:
Define the following term:
spherical mirror
The distance from the center of curvature of the mirror to the pole is called the focal length of the mirror.
