Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
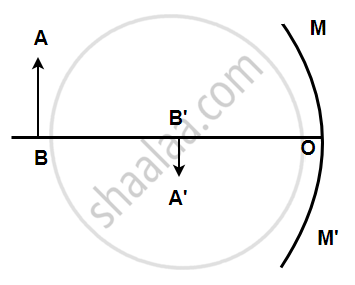
AB is the object, A'B' is the image, and MM' is the position of the mirror. Complete the ray diagram showing the formation of the image and find the focal length of the mirror.
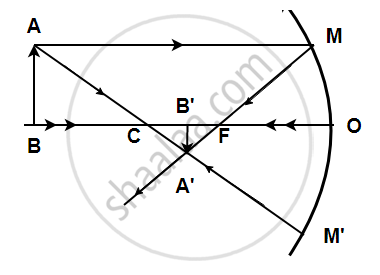
Solution
A light ray coming from a point on object AB is reflected from the surface of the mirror, it passes through the principal focus and the other ray passing through the center of curvature strikes the mirror normally i.e. 90 degrees. Hence it will reflect back. These two reflected rays coincide at a point where the image is formed. The image, A'B' is real, inverted, and diminished in size. The focal length was found to be 16 mm.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The letter F is placed in front of a plane mirror:
What is the name of the phenomenon involved?
The shiny outer surface of a hollow sphere of aluminium of radius 50 cm is to be used as a mirror:
What will be the focal length of this mirror?
Name the kind of mirror used to obtain
(a) a real and enlarged image
(b) a virtual and enlarged image
(c) a real and diminished image, and
(d) a virtual and diminished image.
State the types of mirrors used for (i) headlights and (ii) rear view mirror, in cars and motorcycles. Give to justify your answer in each case.
Which mirror will you prefer to use as a rear view mirror in a car : plane mirror or convex mirror? Give one reason.
An object 5 cm high is placed at a distance 60 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm. Find the position and size of the image.
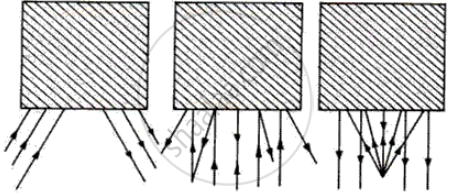
The boxes in figure (a, b, c) represent mirrors; insert a mirror which will reflect the incident ray as shown in the diagram.
Define the term Centre of curvature.
The radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is 18 cm. What is the focal length of this mirror?
A ray of light is incident towards a plane mirror at an angle of 30° with the mirror surface. What will be the angle of reflection?
