Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State the direction of incident ray which after reflection from a spherical mirror gets reflected along its own path. Give a reason.
उत्तर
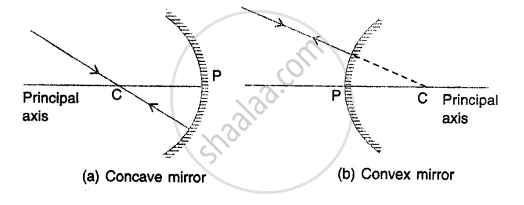
A ray passing through THE CENTRE OF CURVATURE is incident normally on the spherical mirror, gets reflected back along its own path.
A ray passing through the centre of curvature.
It is because the ray is normal to the spherical mirror,
Hence ∠i=0, i.e., the angle of incidence is 0
Therefore, the angle of reflection ∠r=0.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define the terms focus and focal length of a concave mirror. Draw diagram to illustrate your answer.
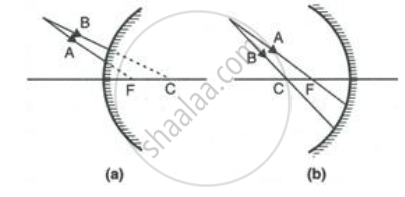
Complete the following diagrams shown in Fig. by drawing the reflected ray for each of the incident ray A and B.
How will you distinguish between a plane mirror, a concave mirror and a convex mirror, without touching them?
An object 5 cm high is placed at a distance 60 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm. Find the position and size of the image.
Draw a ray diagram in each of the following cases to show the formation of image, when the object is placed :
(i) between the optical centre and principal focus of a convex lens.
(ii) anywhere in front of a concave lens.
(iii) at 2F of a convex lens.
State the signs and values of magnifications in the above-mentioned cases (i) and (ii).
An object forms a virtual image which is 1/8th of the size of the object. If the object is placed at a distance of 40 cm from the convex mirror, calculate:
- the position of the image
- the focal length of the convex mirror.
Select the correct option:
Which mirror is used in periscope?
The minimum length of the mirror required to see the full image of the person is half ‘ of his height.
The distance from the center of curvature of the mirror to the pole is called the focal length of the mirror.
In normal adjustment, for a refracting telescope, the distance between objective and eye piece is 30 cm. The focal length of the objective, when the angular magnification of the telescope is 2, will be ______.
