Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Draw a ray diagram in each of the following cases to show the formation of image, when the object is placed :
(i) between the optical centre and principal focus of a convex lens.
(ii) anywhere in front of a concave lens.
(iii) at 2F of a convex lens.
State the signs and values of magnifications in the above-mentioned cases (i) and (ii).
उत्तर
(i) When an object is placed between the optical center and principal focus of a convex lens
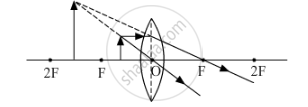
Since the image formed is virtual and erect so sign of magnification will be positive. Moreover, the image formed is magnified therefore the absolute value of magnification will be greater than one.
(ii) When an object is placed anywhere in front of a concave lens.

Since the image formed is virtual and erect so sign of magnification will be positive. Moreover, the image formed is diminished therefore the absolute value of magnification will be less than one.
(iii) When an object is placed at 2F of a convex lens.
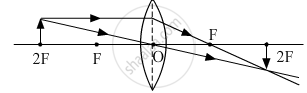
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is the relation between the focal length and radius of curvature of a spherical mirror (concave mirror of convex mirror)? Calculate the focal length of a spherical mirror whose radius of curvature is 25 cm.
Define (a) centre of curvature (b) radius of curvature (c) pole (d) principal axis, and (e) aperture, of a spherical mirror with the help of a labelled diagram
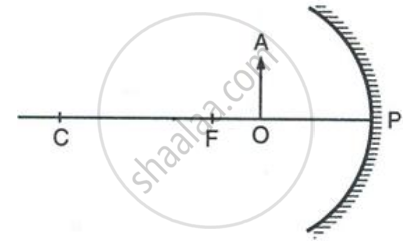
Figure shows a concave mirror with its pole at P, focus F and centre of curvature C. Draw ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object OA.
Name the mirror which always produces an erect and virtual image. How is the size of image related to the size of object?
Select the correct option:
Looking into a mirror one finds her image diminished, the mirror is:
Define the following term in relation to concave mirror.
Pole
Complete the following diagrams shown in the following figures by drawing the reflected rays.

