Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Draw a ray diagram in each of the following cases to show the formation of image, when the object is placed :
(i) between the optical centre and principal focus of a convex lens.
(ii) anywhere in front of a concave lens.
(iii) at 2F of a convex lens.
State the signs and values of magnifications in the above-mentioned cases (i) and (ii).
Solution
(i) When an object is placed between the optical center and principal focus of a convex lens
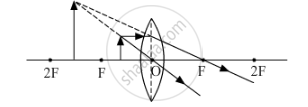
Since the image formed is virtual and erect so sign of magnification will be positive. Moreover, the image formed is magnified therefore the absolute value of magnification will be greater than one.
(ii) When an object is placed anywhere in front of a concave lens.

Since the image formed is virtual and erect so sign of magnification will be positive. Moreover, the image formed is diminished therefore the absolute value of magnification will be less than one.
(iii) When an object is placed at 2F of a convex lens.
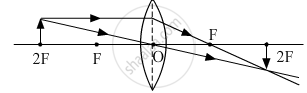
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain the following term related to spherical lenses:- centres of curvature
A virtual image larger than the object can be produced by a ______.
A diverging lens is used in:
(a) a magnifying glass
(b) a car to see objects on rear side
(c) spectacles for the correction of short sight
(d) a simple camera
Name the spherical mirror which (i) diverges (ii) converges the beam of light incident on it. Justify your answer by drawing a ray diagram in each case.
Complete the following diagrams shown in Fig. by drawing the reflected ray for each of the incident ray A and B.
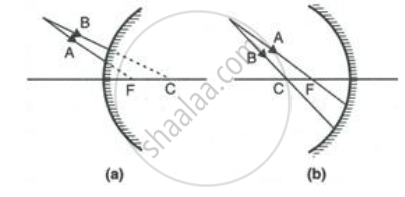
Name the kind of mirror used to obtain:
A virtual and enlarged image
State the kind of mirror used
(a) By a dentist,
(b) As a search-light reflector.
Numerical problem.
The radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is 25 cm. Find its focal length.
Name the two types of spherical mirrors.
