Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Three mirrors are created from a single sphere. Which of the following - pole, centre of curvature, radius of curvature, principal axis - will be common to them and which will not be common?

उत्तर
Let us name the mirrors M1, M2 and M3 as shown below.
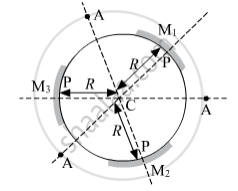
From the figure, we see that
- pole (P) is not common.
- centre of curvature (C) is common.
- principal axis (PA) is not common.
- radius of curvature (R) is common. The radius of curvature is the radius of the sphere. In the given figure, the length CP is the same for all mirrors.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A student focused the Sun rays using an optical device 'X' on a screen S as shown.

From this it may be concluded that the device 'X' is a (select the correct option)
(A) Convex lens of focal length 10 cm.
(B) Convex lens of radius of curvature 20 cm.
(C) Convex lens of focal length 20 cm.
(D) Concave mirror of focal length 20 cm.
Which type of mirror can form a real image?
When a spherical mirror is held towards the sun and its sharp image is formed on a piece of a carbon paper for some time, a hole is burnt in the carbon paper.
What is the advantage of using a carbon paper rather than a white paper?
What is a spherical mirror?
A student obtained on a screen the sharp image of a candle flame placed at the farther end of laboratory table using a concave mirror. For getting better value of focal length of the mirror, the teacher suggested to him to focus the sun. What should the student do?
(A) Should move the mirror away from the screen.
(B) Should move the mirror towards the screen.
(C) Should move the mirror and screen both towards the sun.
(D) Should move only the screen towards the sun.
State the number of images of an object placed between two mirrors, formed in each case when mirrors are inclined to each other at (a) 90°, and (b) 60°.
What is a spherical mirror?
Explain the meaning of the terms focus and focal length in case of a convex mirror, with the help of suitable ray diagram.
Discuss the position and nature of image formed by a convex mirror when an object is moved from infinity towards the pole of mirror.
Which mirror will you prefer to use as a rear view mirror in a car : plane mirror or convex mirror? Give one reason.
A concave mirror forms a virtual image of size twice that of the object placed at a distance 5 cm from it.
Find : (a) the focal length of the mirror (b) position of image
An object 5 cm high is placed at a distance 60 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm. Find the position and size of the image.
Select the correct option:
A mirror forms a virtual image (diminished) of an object, whatever be the position of object:
What do you understand by the term real image?
The boxes in figure (a, b, c) represent mirrors; insert a mirror which will reflect the incident ray as shown in the diagram.
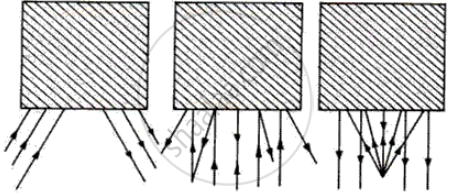
Complete the following diagrams shown in the below figure by drawing the reflected ray for each incident ray.
The spherical mirror used as a rear view mirror in the vehicle is
For a spherical mirror, ______ is true.
