Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
AB and CD, two spherical mirrors, from parts of a hollow spherical ball with its centre at O as shown in the diagram. If arc AB = `1/2` arc CD, what is the ratio of their focal lengths? State which of the two mirrors will always form virtual image of an object placed in front of it and why.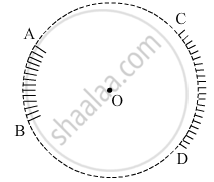
उत्तर
The ratio of the focal lengths of mirrors AB and CD will be equal to one, as both mirrors are part of the same spherical ball. Hence, their radius of curvature and focal length will be the same.
The mirror AB will always form a virtual image when an object is placed in front of it because the mirror AB is a convex mirror.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A concave lens produces an image 20 cm from the lens of an object placed 30 cm from the lens. The focal length of the lens is:
(a) 50 cm
(b) 40 cm
(c) 60 cm
(d) 30 cm
State the direction of incident ray which after reflection from a spherical mirror gets reflected along its own path. Give a reason.
A student obtained on a screen the sharp image of a candle flame placed at the farther end of laboratory table using a concave mirror. For getting better value of focal length of the mirror, the teacher suggested to him to focus the sun. What should the student do?
(A) Should move the mirror away from the screen.
(B) Should move the mirror towards the screen.
(C) Should move the mirror and screen both towards the sun.
(D) Should move only the screen towards the sun.
Complete the following diagrams shown in Fig. by drawing the reflected ray for each of the incident ray A and B.
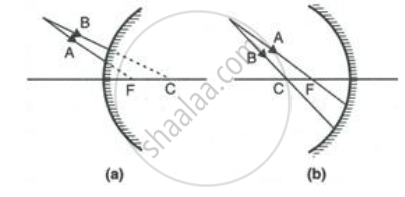
Select the correct option:
A concave mirror is made by cutting a portion of a hollow glass sphere of radius 30 cm. The focal length of the concave mirror is:
Define the following term:
concave mirror
Is real image always inverted?
Name the type of mirror used in the following situation:
Solar furnace
Support your answer with reason.
What is the difference between virtual images of an object formed by a concave mirror and a convex mirror?
