Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
AB and CD, two spherical mirrors, from parts of a hollow spherical ball with its centre at O as shown in the diagram. If arc AB = `1/2` arc CD, what is the ratio of their focal lengths? State which of the two mirrors will always form virtual image of an object placed in front of it and why.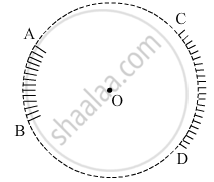
उत्तर
The ratio of the focal lengths of mirrors AB and CD will be equal to one, as both mirrors are part of the same spherical ball. Hence, their radius of curvature and focal length will be the same.
The mirror AB will always form a virtual image when an object is placed in front of it because the mirror AB is a convex mirror.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
We can obtain an enlarged and erect image by a convex mirror.
Define Radius of curvature of the spherical mirror
State the number of images of an object placed between two mirrors, formed in each case when mirrors are inclined to each other at (a) 90°, and (b) 60°.
What is a spherical mirror?
Name the two kinds of spherical mirrors and distinguish between them.
Define the terms focus and focal length of a concave mirror. Draw diagram to illustrate your answer.
Name the kind of mirror used to obtain:
A virtual and enlarged image
Define the following terms in the context of a diverging mirror:
- Principal focus
- Focal length
Draw a labelled ray diagram to illustrate your answer.
