Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Motion in One Dimension
3: Laws of Motion
4: Pressure in Fluids
5: Upthrust and Archimedes’ Principle
6: Heat and Energy
7: Energy Flow and Practices for Conservation of Resources
▶ 8: Light
9: Sound
10: Electricity and Magnetism – 1
11: Electricity and Magnetism – 2
![Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for A New Approach to ICSE Physics Part 1 [English] Class 9 chapter 8 - Light Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for A New Approach to ICSE Physics Part 1 [English] Class 9 chapter 8 - Light - Shaalaa.com](/images/a-new-approach-to-icse-physics-part-1-english-class-9_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 8: Light
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 8 of CISCE Goyal Brothers Prakashan for A New Approach to ICSE Physics Part 1 [English] Class 9.
Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for A New Approach to ICSE Physics Part 1 [English] Class 9 8 Light Unit I Exercise I
What do you understand by the Diffused Light?
What do you understand by the Light?
What is irregular reflection ? Give an example.
By giving one example and one use explain or define Regular reflection.
By drawing a neat diagram define the following:
Mirror
Explain the following term:
Incident ray
Draw diagram/diagrams to show them.
Explain the following term:
Reflected ray
Draw diagram/diagrams to show them.
Explain the following term:
Angle of incidence
Draw diagram/diagrams to show them.
Explain the following term:
Angle of reflection.
Draw diagram/diagrams to show them.
Explain the following term:
Normal Draw
diagram/diagrams to show them.
State the laws of reflection.
A ray of light strikes a plane mirror, such that the angle with the mirror is 20°. What is the value of angle of reflection? What is the angle between the incident ray and the reflected ray?
Prove experimentally that images are formed as far behind in a plane mirror as the object is in front of it.
Prove geometrically that when plane mirror turns through a certain angle, the reflected ray turns through twice the angle.
(a) What do you understand by the term lateral inversion?
(b) A printed card has letters PHYSICS. By drawing the diagram show the appearance of the letters. (No ray diagram is required).
State the mirror formula for the formation of total number of images formed in two plane mirrors, held at an angle.
Calculate the number of images formed in two plane mirrors, when they are held at the angle of (i) 72° (ii) 36°.
Draw a neat two ray diagram for the formation of images in two plane mirrors, when mirrors are at right angles to each other.
Draw a neat two ray diagram for the formation of images in two plane mirrors, when mirrors are at facing each other.
Why are infinite images not seen when two plane mirrors are facing each other?
State four characteristics of the image formed by a plane mirror.
State three ways in which the image formed in a plane mirror differs from the image formed in a pin hole camera.
What should be the minimum size of a plane mirror, so that a person 182 cm high can see himself completely?
A boy stands 4 m away from the plane mirror. If the boy moves `1/2` m towards the mirror, what is now the distance between the boy and his image? Give a reason for your answer.
State four uses of a plane mirror.
Draw a neat diagram of reflecting periscope.
State two advantages and two disadvantages of the reflecting periscope.
What must be the minimum length of a plane mirror in which a person can see himself full length? Draw a diagram to justify your answer. Does the distance of a person from the mirror affect the above answer?
An insect is sitting in front of a plane mirror at a distance of one meter from it.
- Where is the image of insect formed?
- What is the distance between insect and its image?
- State any two characteristics of image formed in a plane mirror.
Draw a diagram to show the reflection of a ray of light using a plane mirror. In the diagram, label the incident ray, the reflected ray, the normal, the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection.
State the laws of reflection.
Parallel rays are incident:
- on regular surface and
- on irregular surface. In what respect do reflected rays in (1) differ from those of (2)?
Write down four characteristics of image formed in a plane mirror.
How many images will be formed when an object is placed between two parallel plane mirrors with their reflecting surfaces facing each other? Why do more distant images appear fainter?
Write down the letters of the word ‘POLEX’ as seen in a plane mirror, held parallel to the plane of this paper.
Distinguish between real and virtual image.
Describe the principle of simple periscope through an outline ray diagram. Give one of its uses.
Draw diagrams to show the difference between regular and irregular reflection.
An object is placed 2 cm from a plane mirror. If the object is moved by 1 cm towards the mirror, what will be the distance between the object and its new image?
Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for A New Approach to ICSE Physics Part 1 [English] Class 9 8 Light Unit II Practice Problem 1
An object 3 cm high produces a real image 4.5 cm high when placed at a distance of 20 cm from a concave mirror. Calculate:
- the position of image
- focal length of the concave mirror.
Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for A New Approach to ICSE Physics Part 1 [English] Class 9 8 Light Unit II Practice Problem 2
An object 1.5 cm high when placed in front of a concave. the mirror produces a virtual image 3 cm high. If the object is placed at a distance of 6 cm from the pole of the mirror, calculate:
- the position of the image
- the focal length of the mirror.
A converging mirror, forms three times magnified virtual image when an object is placed at a distance of 8 cm from it. Calculate:
- the position of the image
- the focal length of the mirror.
Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for A New Approach to ICSE Physics Part 1 [English] Class 9 8 Light Unit II Practice Problem 3
An object 5 cm high forms a virtual image of 1.25 cm high, when placed in front of a convex mirror at a distance of 24 cm. Calculate:
- the position of the image
- the focal length of the convex mirror.
An object forms a virtual image which is 1/8th of the size of the object. If the object is placed at a distance of 40 cm from the convex mirror, calculate:
- the position of the image
- the focal length of the convex mirror.
Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for A New Approach to ICSE Physics Part 1 [English] Class 9 8 Light Exercise II Objective Questions
Select the correct option:
A concave mirror is made by cutting a portion of a hollow glass sphere of radius 30 cm. The focal length of the concave mirror is:
24 cm
12 cm
15 cm
60 cm
Select the correct option:
A mirror forms a virtual image (diminished) of an object, whatever be the position of object:
it must be a concave mirror
it must be a convex mirror
it must be a plane mirror
it may be convex mirror or plane mirror
Select the correct option:
A ray of light is incident on a concave mirror. If it is parallel to principal axis, the reflected ray will:
pass through its principal focus
pass through its centre of curvature
pass through its pole
retraces its path
Select the correct option:
If an incident ray passes through the centre of curvature of a spherical mirror, the reflected ray will:
pass through its pole
retraces its path
pass through its focus
be parallel to principal axis
Select the correct option:
In case of concave mirror, the minimum distance between an object and its real image is:
f
2f
4f
zero
Select the correct option:
Looking into a mirror one finds her image diminished, the mirror is:
concave
convex
cylindrical
parabolic
Select the correct option:
Which mirror is used in periscope?
concave mirror
convex mirror
Plane mirror
parabolic mirror
Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for A New Approach to ICSE Physics Part 1 [English] Class 9 8 Light Exercise II Subjective Questions
Define the following term:
spherical mirror
Define the following term:
convex mirror
Define the following term:
concave mirror
Define the following term in relation to concave mirror.
Pole
Define the following term in relation to concave mirror.
Center of curvature
Define the following term in relation to concave mirror.
Principal axis
Define the following term in relation to concave mirror.
Principal focus
Define the following term in relation to concave mirror.
Focal length
Define the following term in relation to concave mirror.
Radius of curvature
Define the following term in relation to concave mirror.
Aperture
Define the term principal focus in case of convex mirror. Draw a convex mirror and show its principal focus and focal length clearly.
What is the relation between focal length and radius of curvature of a concave mirror?
What do you understand by the term real image?
What type of mirror can be used to obtain a real image of an object?
Does the mirror name by your form a real image for all locations? Give a reason for your answer.
Is real image always inverted?
Copy the figure. By taking two rays from point A, show the formation of image. State four characteristics of the image.
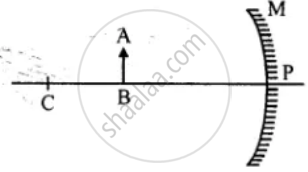
Draw a neat two ray diagram to illustrate how a concave mirror is used as a shaving mirror.
Copy the figure. By taking two rays from point A, show the formation of image. State four characteristics of the image.
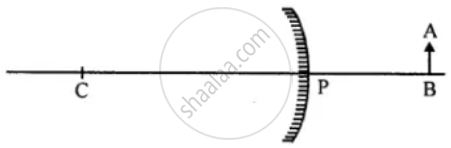
Why do automobile drivers prefer convex mirror as a rear vew mirror? Illustrate your answer.
Give two uses of convex mirror.
Give two uses of concave mirror.
You are provided a convex mirror, a concave mirror and a plane mirror. How will you distinguish between them, without touching or using any other apparatus?
Compare the characteristics of an image formed by a convex mirror and a concave mirror, when object is beyond center of curvature, but not at infinity.
Why does a driver use a convex mirror instead of a plane mirror as a rear view mirror?
Illustrate your answer with the help of a ray diagram.
What is a real image?
What type of mirror is used to obtain a real image-of an object?
Does the mirror named by you above give real images for all locations of object?
In the figure is shown a concave mirror. A is a point on the principal axis. If an object O is kept at A, image is formed on A itself. Copy the diagram. Draw the image in the diagram. Is the image real or virtual?
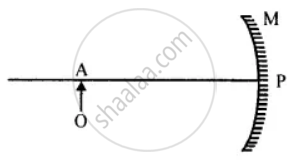
Measure the distance PA and write it in the diagram. What is the distance PA called?
Mark a point B on the principal axis, at which, if a point source of light is kept, the rays travel parallel to principal axis after reflection from M. What is point B called?
An object OA is placed on the principal axis of a concave mirror as shown in the figure. Copy and complete the diagram to show the formation of image.
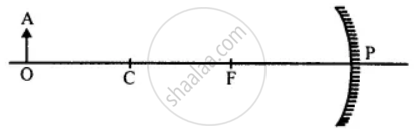
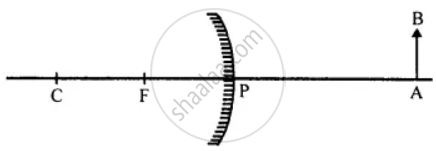
Copy the figure and complete it, by drawing two rays to show the formation of the image of the object AB. State the size, position and nature of image formed.
Solutions for 8: Light
![Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for A New Approach to ICSE Physics Part 1 [English] Class 9 chapter 8 - Light Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for A New Approach to ICSE Physics Part 1 [English] Class 9 chapter 8 - Light - Shaalaa.com](/images/a-new-approach-to-icse-physics-part-1-english-class-9_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for A New Approach to ICSE Physics Part 1 [English] Class 9 chapter 8 - Light
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics A New Approach to ICSE Physics Part 1 [English] Class 9 CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for Mathematics A New Approach to ICSE Physics Part 1 [English] Class 9 CISCE 8 (Light) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Goyal Brothers Prakashan textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in A New Approach to ICSE Physics Part 1 [English] Class 9 chapter 8 Light are Rules for the Construction of Image Formed by a Spherical Mirror, Focus and Focal Length, Images Formed by Spherical Mirrors, Concave Mirror, Image Formation by Concave Mirror, Convex Mirror, Mirror Equation/Formula, Images Formed by a Plane Mirrors, Distinction Between a Plane Mirror, Concave Mirror and Convex Mirror, Images Formed in a Pair of Mirrors Placed Parallel to Each Other, Images Formed by Two Mirrors Placed Perpendicular to Each Other, Spherical Mirrors, Image Formation by Convex Mirror, Relationship Between the Focal Length and Radius of Curvature, Sign Convention, Reflection of Light, Types of Reflection, Terms Used in Reflection of Light, Law of Reflection of Light, Verification of the Law of Reflection of Light, Formation of Image by Reflection: Real and Virtual Image, Formation of Image of a Point Object by a Plane Mirror, Image of an Extended Object Formed by a Plane Mirror, Position of Image, Lateral Inversion, Plane Mirror, Images Formed in Two Inclined Mirrors.
Using Goyal Brothers Prakashan A New Approach to ICSE Physics Part 1 [English] Class 9 solutions Light exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Goyal Brothers Prakashan Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE A New Approach to ICSE Physics Part 1 [English] Class 9 students prefer Goyal Brothers Prakashan Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 8, Light A New Approach to ICSE Physics Part 1 [English] Class 9 additional questions for Mathematics A New Approach to ICSE Physics Part 1 [English] Class 9 CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
