Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State the two convenient rays that are chosen to construct the image by a spherical mirror for a given object? Explain your answer with the help of suitable ray diagrams.
उत्तर
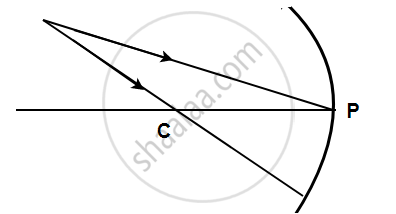
Two convenient rays that are chosen to construct the image by a spherical mirror for a given object:
- A ray passing through the centre of curvature:A ray of light passing through the centre of curvature of a concave mirror or a ray directed in the direction of centre of curvature of a convex mirror is reflected back along the same path after reflection.
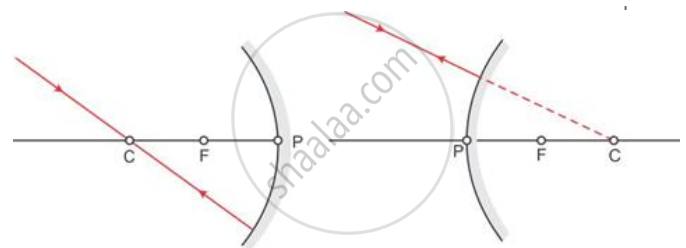
2. A ray parallel to the principal axis: A ray of light parallel to the principal axis, after reflection pass through the principal focus in case of a concave mirror or appears to diverge from it in case of convex mirror.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A student focused the Sun rays using an optical device 'X' on a screen S as shown.

From this it may be concluded that the device 'X' is a (select the correct option)
(A) Convex lens of focal length 10 cm.
(B) Convex lens of radius of curvature 20 cm.
(C) Convex lens of focal length 20 cm.
(D) Concave mirror of focal length 20 cm.
Define the following term in the context of spherical mirrors:- Centre of curvature
What do you understand by the focus and focal length of a spherical mirror? Show them on the separate diagrams for each of a concave mirror and a convex mirror.
An object of height 2 cm is placed at a distance of 20 cm in front of a concave mirror of a focal length of 12 cm. Find the position, size, and nature of the image.
Draw a ray diagram in each of the following cases to show the formation of image, when the object is placed :
(i) between the optical centre and principal focus of a convex lens.
(ii) anywhere in front of a concave lens.
(iii) at 2F of a convex lens.
State the signs and values of magnifications in the above-mentioned cases (i) and (ii).
In the following figure shows a concave mirror with its pole (P), focus (F) and centre of curvature (C). Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image of an object AB by the concave mirror.
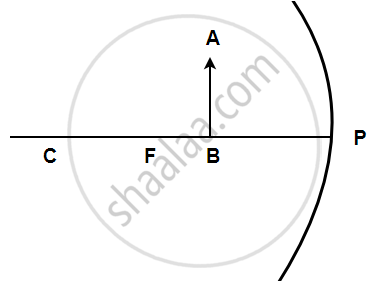
Complete the following diagrams shown in the following figures by drawing the reflected rays.