Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
उत्तर
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
We can obtain a real, enlarged and inverted image by a concave mirror.
A virtual image larger than the object can be produced by a ______.
AB and CD, two spherical mirrors, from parts of a hollow spherical ball with its centre at O as shown in the diagram. If arc AB = `1/2` arc CD, what is the ratio of their focal lengths? State which of the two mirrors will always form virtual image of an object placed in front of it and why.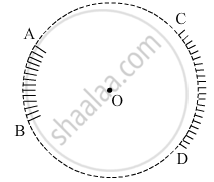
State the position of object for which the image formed by a concave mirror is of same size.
Why does a driver use a convex mirror instead of a plane mirror as a rear view mirror?
Illustrate your answer with the help of a ray diagram.
Upto what maximum distance from a concave mirror, the image can be obtained? What will be the location of object for it?
An object of length 4 cm is placed in front of a concave mirror at distance 30 cm. The focal length of mirror is 15 cm.
- Where will the image form?
- What will be the length of image?
The radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is 18 cm. What is the focal length of this mirror?
A spherical mirror whose reflecting surface is curved outwards is called ______ mirror.
A converging lens of focal length f is placed at a distance 0.3 m from an object to produce an image on a screen 0.9 m from the lens. With the object and the screen in the same positions, an image of the object could also be produced on the screen by placing a converging lens of focal length.
