Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Motion in One Dimension
3: Laws of Motion
4: Fluids
5: Heat
6: Light
7: Sound
▶ 8: Electricity and Magnetism
![Frank solutions for Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 8 - Electricity and Magnetism Frank solutions for Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 8 - Electricity and Magnetism - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-english-class-9-icse_6:1a0f7706074c4feda1fb5ca0ff12ac66.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 8: Electricity and Magnetism
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 8 of CISCE Frank for Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE.
Frank solutions for Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE 8 Electricity and Magnetism Static Electricity [Pages 300 - 302]
State the kind of charge on a positive ion.
State the kind of charge on a negative ion.
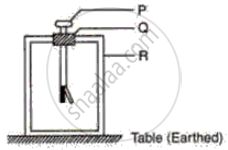
The following Figure represents a negatively charged gold Ieaf electroscope. Label the parts, P, Q, and R and the estate whether each is an insulator or a conductor. Also, indicate the distribution of charges on the system in the diagram.
The following figure shows a metal rod PQ mounted on an insulated stand. The cap of an uncharged electroscope touches one end Q of the metal rod. A negatively charged ebonite rod is brought near the other end P of the metal rod.
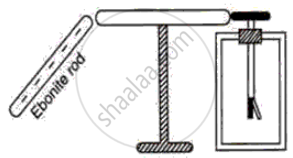
(a) What charge does the end P have?
(b) What charge does the end Q have?
(c) What charge does the cap of the electroscope have?
(d) What charge does the gold leaf have?
(e) Will the leaf diverge or collapse? Give reason.
(f) If the electroscope is now earthed, what charge does the metal rod have?
Frank solutions for Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE 8 Electricity and Magnetism Current Electricity [Pages 312 - 313]
What do you mean by an electric current?
What is an electric cell?
How much is the charge on an electron?
Name the constituents of a cell.
Write SI unit of
Electric current,
Write SI unit of
Potential difference
Write SI unit of
Resistance.
What is the number of electrons that would flow per second through the cross-section of a wire when 1 A current flows in it?
0.7 C charges passes through a cross-section of a conductor in 7 s. Find the current.
Name the instrument used to control current in an electric circuit.
What is the other name of a variable resistor?
What is the function of a switch in an electric circuit?
Write symbol and state function of following component in an electric circuit :
cell
Write symbol and state function of following component in an electric circuit :
ammeter
Write symbol and state function of following component in an electric circuit :
voltmeter
Write symbol and state function of following component in an electric circuit : key
battery
Write symbol and state function of following component in an electric circuit :
rheostat
A current of 1.2 A flows through a conductor for 3.0 s. What amount of charge passes through the conductor?
Label the different parts A, B, C, D, E, and F. State the functions of each part. Show in the diagram the direction of flow of current.
l-V graph is shown for a good conductor. What does the slope of the graph represent?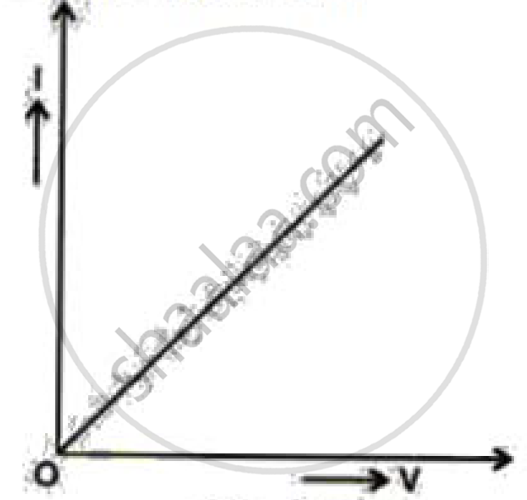
What do you mean by the potential difference? Write its SI unit.
Is electric current a scalar quantity?
State the factors on which the electrical resistance of a wire depends.
What is the SI unit of resistance?
A bulb is connected to a cell. How is the resistance of circuit affected if another identical bulb is connected (i) in series, (ii) in parallel, with the first bulb?
How are the potential difference (V), current (l) and resistance (R) related?
'The resistance of a wire is 2 ohm'. Explain the meaning of this statement.
Write symbol and state function of following component in an electric circuit :
cell
Write symbol and state function of following component in an electric circuit :
ammeter
Write symbol and state function of following component in an electric circuit :
voltmeter
Write symbol and state function of following component in an electric circuit : key
battery
Write symbol and state function of following component in an electric circuit :
rheostat
State three factors on which the resistance of a wire depends. Explain, how does the resistance depend on the factors stated by you.
What amount of work is required in moving 3 C charge through a potential difference of 6 V?
What is the physical meaning of resistance?
'The potential difference between two conductors is 1 volt'. Explain the meaning of this statement.
Frank solutions for Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE 8 Electricity and Magnetism Magnestism [Page 320]
Define the term Magnetic axis
Define the term Poles of a magnet
Define the term Effective length of a magnet
Different bars are brought near each pole of a compass needle. Complete the following table:
| Nature of bar | Action on the compass needle | |
| North pole | South pole | |
| (i) Glass | No action | __________ |
| (ii) _________ | Attracted | Attracted |
| (iii) North pole of a bar magnet | __________ | ___________ |
| (iv) The south pole of a bar magnet | __________ | repulsion |
Frank solutions for Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE 8 Electricity and Magnetism Exercise [Pages 323 - 325]
Name the instrument used to control the current in an electric circuit.
A wire of resistance 1 Ω is stretched to double its length. What will happen to the resistance of the stretched wire?
What is a natural magnet?
State three important properties of a magnet.
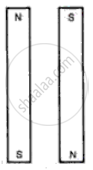
A magnet is carefully broken into two halves along its long axis as shown in the figure. How would the magnetic strength of each piece compare with that of the original magnet?
A magnet is carefully broken into two equal pieces as shown in the figure. How would the magnetic field strength of each piece compare with that of the original magnet? 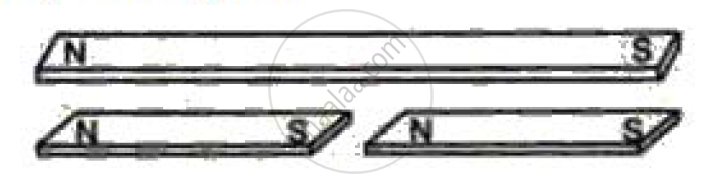
A conductor B is charged by bringing another charged body A in contact 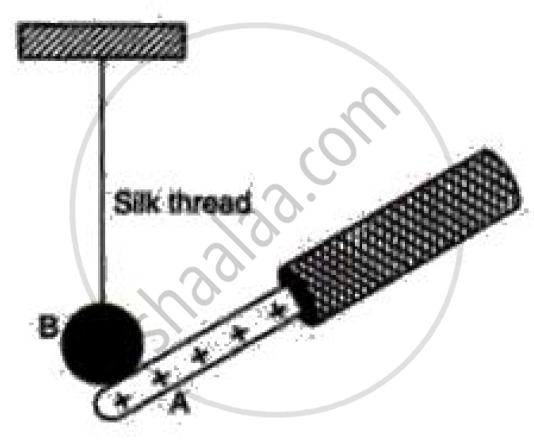
What will be the charge gained by B?
A conductor B is charged by bringing another charged body A in contact 
Explain the process of charging B.
What is an electroscope? Describe the different stages of charging a gold leaf electroscope negatively with the help of a diagram.
What is meant by electrostatic induction? You have been given two metal containers A and Band a positively charged body X. With the help of a diagram, explain the different stages of charging - A positively, and B negatively.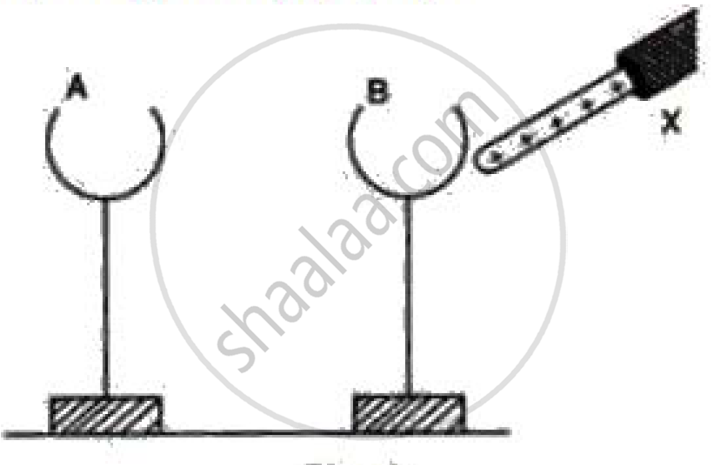
Write a short note on lighting conductors.
Explain the following:
Resistance of a conductor
Explain the following:
Potential difference
Explain the following:
Open circuit
Explain the following:
Closed circuit
Compare the brightness of two 60 watt bulbs.
When they are connected in series.
Explain giving scientific reasons.
Compare the brightness of two 60 watt bulbs.
When they are connected in parallel.
Explain giving scientific reasons.
Differentiate between:
Conductors and insulators.
Differentiate between:
Flow of electron and flow of conventional current.
Differentiate between:
Primary and secondary cell.
What are the properties of a magnet?
State the laws of magnetism.
Distinguish between
Magnetic and non-magnetic materials.
Distinguish between
Natural and artificial magnets.
Distinguish between
Magnetic properties of iron and steel.
With the help of a diagram explain the following:
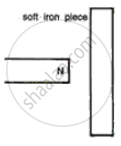
Magnetisation of an iron bar by a single touch method.
With the help of a diagram explain the following:
Magnetisation of steel needle using electric current such that the pointed end should have north polarity.
Explain, what is meant by magnetic induction.
How would you test whether a piece of steel was magnetised
(i) If you had a magnet?
(ii) If there was no magnet available.
Define the following term:
Geographic meridian
Define the following term:
Angle of declination
Define the following term:
Angle of dip
Define the following term:
Magnetic meridian
Give scientific reason:
A ' cracking' noise may be heard on removing a nylon shirt, blouse, or stockings.
Give scientific reason:
A charge can be obtained on a rubbed ebonite rod held in the hand but not on a rubbed metal rod held in the hand.
Give scientific reason:
Soft iron is used to make electromagnets.
Give scientific reason:
Two steel needles hanging from the lower end of a vertical bar magnet do not hang vertically.
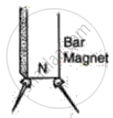
Give scientific reason:
Not attraction but repulsion is a sure test of magnetism.
What is a neutral point?
Draw the magnetic field lines around a bar magnet when a bar magnet is placed such that the N pole points North.
Suggest the best particles in the use of energy at school.
Suggest the best particles in the use of energy at home that save energy.
Complete the following diagram of magnets to show the lines of force.
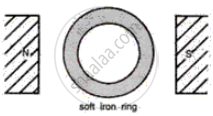
Complete the following diagram of magnets to show the lines of force.

Complete the following diagram of magnets to show the lines of force.
Complete the following diagram of magnets to show the lines of force.
Solutions for 8: Electricity and Magnetism
![Frank solutions for Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 8 - Electricity and Magnetism Frank solutions for Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 8 - Electricity and Magnetism - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-english-class-9-icse_6:1a0f7706074c4feda1fb5ca0ff12ac66.jpg)
Frank solutions for Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 8 - Electricity and Magnetism
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Frank solutions for Mathematics Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE CISCE 8 (Electricity and Magnetism) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Frank textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 8 Electricity and Magnetism are Electric cell, Symbols and Functions of Various Components of an Electric Circuits, Direction of the Electric Current - Conventional and Electronic Flow, Conservation of Electrical Energy, Electric Current, Electric Circuit, Types of Circuits: Simple Circuit, Conductors and Insulators, Flow of Charges (Electrons) Between Conductor, Potential and Potential Difference, Resistance (R), Ohm's Law (V = IR), Social Initiatives for Energy, Factors Affecting the Resistance of a Conductor.
Using Frank Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE solutions Electricity and Magnetism exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Frank Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE students prefer Frank Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 8, Electricity and Magnetism Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE additional questions for Mathematics Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
