Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Name the spherical mirror which can produce a real and diminished image of an object.
उत्तर
Only a concave mirror can produce a real and diminished image of an object.
संबंधित प्रश्न
One half of a convex lens of focal length 10 cm is covered with a black paper. Can such a lens produce an image of a complete object placed at a distance of 30 cm from the lens? Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer. A 4 cm tall object is placed perpendicular to its principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 15 cm. Find the nature, position and the size of the image.
A student focused the Sun rays using an optical device 'X' on a screen S as shown.

From this it may be concluded that the device 'X' is a (select the correct option)
(A) Convex lens of focal length 10 cm.
(B) Convex lens of radius of curvature 20 cm.
(C) Convex lens of focal length 20 cm.
(D) Concave mirror of focal length 20 cm.
Define the following term in the context of spherical mirrors:- Principal focus
Explain the following term related to spherical lenses:- principal axis
Explain the following term related to spherical lenses: focal length
Which are the two convenient rays that are chosen to construct the image by a spherical mirror for a given object? Explain with the help of suitable ray diagrams.
An optical device has been given to a student and he determines its focal length by focusing the image of the sun on a screen placed 24 cm from the device on the same side as the sun. Select the correct statement about the device.
(A) Convex mirror of focal length 12 cm
(B) Convex lens of focal length 24 cm
(C) Concave mirror of focal length 24 cm
(D) Convex lens of focal length 12 cm
AB and CD, two spherical mirrors, from parts of a hollow spherical ball with its centre at O as shown in the diagram. If arc AB = `1/2` arc CD, what is the ratio of their focal lengths? State which of the two mirrors will always form virtual image of an object placed in front of it and why.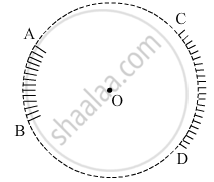
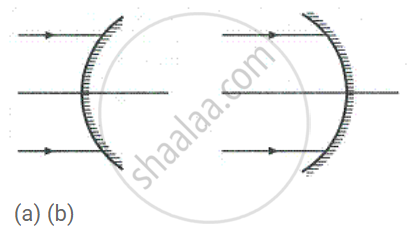
Name the mirrors shown in Figure (a) and (b).
Complete the following diagrams in Figure by drawing the reflected rays for the incident rays 1 and 2.
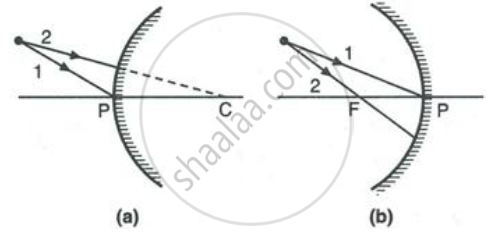
State the two convenient rays that are chosen to construct the image by a spherical mirror for a given object? Explain your answer with the help of suitable ray diagrams.
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image by a concave mirror for the object beyond its centre of curvature. State three characteristics of the image.
What type of mirror can be used to obtain a real image of an object?
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object kept in front of a convex mirror. State three characteristics of the image.
Select the correct option:
A mirror forms a virtual image (diminished) of an object, whatever be the position of object:
Assertion: Incident ray is directed towards the centre of curvature of spherical mirror. After reflection it retraces its path.
Reason: Angle of incidence (i) = Angle of reflection (r) = 0°
A shopkeeper wanted to fix a mirror that will give a maximum view of his shop. What type of mirror should he use? Give reason.
How tall does a mirror have to be to fit an entire person’s body?
