Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Using Huygens's construction, show how a plane wave is reflected from a surface. Hence verify the law of reflection.
Solution
Laws of reflection:
- 1st law: It claims that the angle of incidence and angle of reflection are equal.
- 2nd law: According to this statement, the incident ray, the reflected ray, and the incident point normal all lie in the same plane.

The first law of reflection. Let XY be a plane reflecting surface and AB be a plane wavefront incident on the surface as shown in the figure.
According to the Huygens principle, every point on wavefront AB is a source of secondary wavelet and the time during which wavelet from reaches C, the reflected wavelet from A would arrive at D.
i.e. `t = (BC)/v = (AD)/v`
or BC = AD ...............(i)
`v` = velocity of light in the medium
In a right-angled triangle ΔABC,
`sini = (BC)/(AC)`
or BC = AC sini ..............(ii)
In ΔADC
`sinr = (AD)/(AC)`
or AD = AC sinr .........(iii)
Putting equations (ii) and (iii) in (i), we get
AC sini = AC sinr
sini = sinr
or i = r
This is the first law of reflection.
In the second law of reflection, from the figure we find that the incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal all lie on the same plane XY. This proves the second law of reflection.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Light of wavelength 5000 Å falls on a plane reflecting surface. What are the wavelength and frequency of the reflected light? For what angle of incidence is the reflected ray normal to the incident ray?
The propagation of light is best described by ______.
The quantity which does NOT change during reflection is ______.
An air bubble in glass slab (µ = 1.5) when viewed from one side, appears to be at 6 cm and from opposite side 4 cm. The thickness of glass slab is ______.
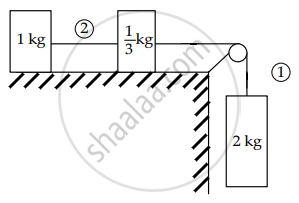
All the surfaces are frictionless. Strings are light and frictionless. The tension in string 1 is ______ N. (Take g = 10 m/s2)
If the critical angle for total internal reflection from a medium to vacuum is 30°, the velocity of light in the medium is ______.
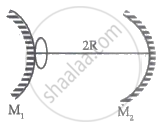
Two spherical mirrors, one convex and the other concave, each of same radius of curvature R are arranged coaxially at a distance of 2R from each other. A small circle of radius a is drawn on the convex mirror as shown in figure. What is the radii of first two images of the circle?
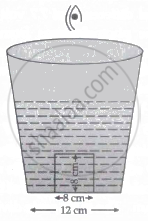
A cylindrical vessel of diameter 12 cm contains 800π cm3 of water. A cylindrical glass piece of diameter 8.0 cm and height 8.0 cm is placed in the vessel. If the bottom of the vessel under the glass piece is seen by the paraxial rays, locate its image from bottom. The index of refraction of glass is 1.50 and that of water is 1.33.
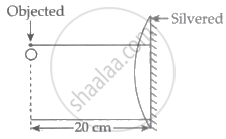
An object O is placed at a distance of 20 cm from a thin plano-convex lens of a focal length of 15 cm. The place surface of the lens is silvered as shown in the figure. The image is formed at a distance of ______.
With the help of a diagram, show how a plane wave is reflected from a surface. Hence verify the law of reflection.
