Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
With the help of a diagram, show how a plane wave is reflected from a surface. Hence verify the law of reflection.
Solution
According to the laws of reflection:
- At the point of incidence, the incident rays, reflected rays, and normal to the reflecting surface all lie in the same plane.
- On opposing sides of the normal are the incident and reflected rays.
- The angle of incidence and the angle of reflection are the same. i.e., ∠i = ∠r.
Explanation:

Reflection of light
XY: Plane reflecting surface
AB: Plane wavefront
RB1: Reflecting wavefront
A1M, B1N: Normal to the plane
∠AA1M = ∠BB1N = ∠i = Angle of incidence
∠TA1M = ∠QB1N = ∠r = Angle of reflection
- A plane wavefront AB is advancing obliquely towards the plane reflecting surface XY. AA1 and BB1 are incident rays.
- When ‘A’ reaches XY at A1, then the ray at ‘B’ reaches point 'P’ and it has to cover distance PB1 to reach the reflecting surface XY.
- Let 't' be the time required to cover distance PB1. During this time interval, secondary wavelets are emitted from A1 and will spread over a hemisphere of radius A1R, in the same medium. The distance covered by secondary wavelets to reach from A1 to R in time t is the same as the distance covered by primary waves to reach from P to B1. Thus A1R = PB1 = ct.
- All other rays between AA1 and BB1 will reach XY after A1 and before B1. Hence they will also emit secondary wavelets of decreasing radii.
- The surface touching all such hemispheres is RB1 which is the reflected wavefront, bounded by reflected rays A1R and B1Q.
- Draw A1M ⊥ XY and B1N ⊥ XY.
Thus, the angle of incidence is ∠AA1M = ∠BB1N = i and the angle of reflection is ∠MA1R = ∠NB1Q = r.
∠RA1B1 = 90 - r
∠PB1A1 = 90 - i
In ΔA1RB1 and ΔA1PB1
∠A1RB1 = ∠A1PB1
A1R = PB1 ....(Reflected waves travel an equal distance in the same medium in equal time.)
A1B1 = A1B1 ....(Common side)
∴ ΔA1RB1 ≅ ΔA1PB1
∴ ∠RA1B1 = ∠PB1A1
∴ 90 - r = 90 - i
∴ i = r - Also from the figure, it is clear that incident rays, reflected rays and normal lie in the same plane.
- This explains the laws of reflection of light from a plane reflecting surface on the basis of Huygens' wave theory.
Note:
- Frequency, wavelength and speed of light do not change after reflection.
- If reflection takes place from a denser medium, then the phase changes by π radians.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Light of wavelength 5000 Å falls on a plane reflecting surface. What are the wavelength and frequency of the reflected light? For what angle of incidence is the reflected ray normal to the incident ray?
The propagation of light is best described by ______.
The quantity which does NOT change during reflection is ______.
An air bubble in glass slab (µ = 1.5) when viewed from one side, appears to be at 6 cm and from opposite side 4 cm. The thickness of glass slab is ______.
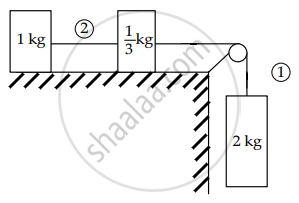
All the surfaces are frictionless. Strings are light and frictionless. The tension in string 1 is ______ N. (Take g = 10 m/s2)
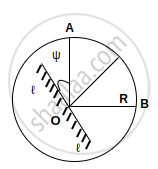
The mirror of length 2l makes 10 revolutions per minute about the axis crossing its mid-point O and perpendicular to the plane of the figure There is a light source in point A and an observer at point B of the circle of radius R drawn around centre O (∠AOB = 90°) What is the proportion `"R"/ℓ` if the observer B first sees the light source when the angle of mirror ψ = 15°?
If the critical angle for total internal reflection from a medium to vacuum is 30°, the velocity of light in the medium is ______.
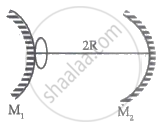
Two spherical mirrors, one convex and the other concave, each of same radius of curvature R are arranged coaxially at a distance of 2R from each other. A small circle of radius a is drawn on the convex mirror as shown in figure. What is the radii of first two images of the circle?
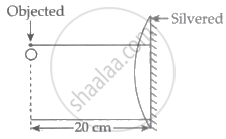
An object O is placed at a distance of 20 cm from a thin plano-convex lens of a focal length of 15 cm. The place surface of the lens is silvered as shown in the figure. The image is formed at a distance of ______.
Using Huygens's construction, show how a plane wave is reflected from a surface. Hence verify the law of reflection.
