Science (English Medium)
Academic Year: 2022-2023
Date & Time: 6th March 2023, 10:30 am
Duration: 3h
Advertisements
General Instructions:
Read the following instructions very carefully and strictly follow them:
- This question paper contains 35 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- Question paper is divided into FIVE sections - Section A, B, C, D and E.
- Section A: Question number 1 to 18 are Multiple Choice (MCQ) type questions carrying 1 mark each:
- Section B: Question number 19 to 25 are Short Answer-1 (SA-1) type questions carrying 2 marks each.
- Section C: Question number 26 to 30 are Short Answer-2 (SA-2) type questions carrying 3 marks each
- Section D: Question number 31 to 33 are Long Answer (LA) type questions carrying 5 marks each.
- Section E: Question number 34 and 35 are Case-Based questions carrying 4 marks each.
- There is no over all choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in 2 questions in Section-B, 2 questions in Section-C, 3 questions in Section-D and 2 questions in Section E.
- Use of calculators is NOT allowed.
- c = 3 × 108 m/s
h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js
e = 1.6 × 10-19C
μ0 = 4π × 10-7T m A-1
ε0 = 8.854 × 10-12C2N-1m-2
`1/(4piε_0) = 9 xx 10^9 Nm^2C^-2`
Mass of electron = (me) = 9.1 × 10-31 kg
Mass of Neutron = 1.675 × 10-27kg
Mass of proton = 1.673 × 10-27kg
Avogadro's number = 6.023 × 1023 per gram mole
Boltzmann constant = 1.38 × 10-23 Jk-1
- c = 3 × 108 m/s
The ratio of the magnitudes of the electric field and magnetic field of a plane electromagnetic wave is ______.
1
`1/c`
c
`1/c^2`
Chapter: [0.08] Electromagnetic Waves
Specify the transition of an electron in the wavelength of the line in the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom which gives rise to the spectral line of the highest wavelength ______.
n = 3 to n = 1
n = 3 to n = 2
n = 4 to n = 1
n = 4 to n = 2
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
A current of 0.8 A flows in a conductor of 40 Ω for 1 minute. The heat produced in the conductor will be ______.
1445 J
1536 J
1569 J
1640 J
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
A cell of emf E is connected across an external resistance R. When current 'I' is drawn from the cell, the potential difference across the electrodes of the cell drops to V. The internal resistance 'r' of the cell is ______.
`((E - V)/E)R`
`((E - V)/R)`
`((E - V)R)/I`
`((E - V)/V)R`
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
An isolated point charge particle produces an electric field `vecE` at a point 3 m away from it. The distance of the point at which the field is `vecE/4` will be ______.
2 m
3 m
4 m
6 m
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
A long straight wire of radius 'a' carries a steady current 'I'. The current is uniformly distributed across its area of cross-section. The ratio of the magnitude of magnetic field `vecB_1` at `a/2` and `vecB_2` at distance 2a is ______.
`1/2`
1
2
4
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
A steady current of 8 mA flows through a wire. The number of electrons passing through a cross-section of the wire in 10 s is ______.
4.0 × 1016
5.0 × 1017
1.6 × 1016
1.0 × 1017
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
Which one of the following elements will require the highest energy to take out an electron from them?
Pb, Ge, C and Si
Ge
C
Si
Pb
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
A conductor of 10 Ω is connected across a 6 V ideal source. The power supplied by the source to the conductor is ______.
1.8 W
2.4 W
3.6 W
7.2 W
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Which one of the following metals does not exhibit emission of electrons from its surface when irradiated by visible light?
Rubidium
Sodium
Cadmium
Caesium
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
A hydrogen atom makes a transition from n = 5 to n = 1 orbit. The wavelength of photon emitted is λ. The wavelength of photon emitted when it makes a transition from n = 5 to n = 2 orbit is ______.
`8/7lambda`
`16/7lambda`
`24/7lambda`
`32/7lambda`
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
A photon of wavelength 663 nm is incident on a metal surface. The work function of the metal is 1.50 eV. The maximum kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons is ______.
3.0 × 10-20 J
6.0 × 10-20 J
4.5 × 10-20 J
9.0 × 10-20 J
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
In an extrinsic semiconductor, the number density of holes is 4 × 1020 m-3. If the number density of intrinsic carriers is 1.2 × 1015 m-3, the number density of electrons in it is ______.
1.8 × 109 m-3
2.4 × 1010 m-3
3.6 × 109 m-3
3.2 × 1010 m-3
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
A ray of light of wavelength 600 nm propagates from air into a medium. If its wavelength in the medium becomes 400 nm, the refractive index of the medium is ______.
1.4
1.5
1.6
1.8
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
The formation of the depletion region in a p-n junction diode is due to ______.
movement of dopant atoms
diffusion of both electrons and holes
drift of electrons only
the drift of holes only
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
- Assertion (A): Work done in moving a charge around a closed path, in an electric field is always zero.
- Reason (R): Electrostatic force is a conservative force.
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is NOT the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Assertion (A) is true and Reason (R) is false.
Assertion (A) is false and Reason (R) is also false.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
- Assertion (A): In Young's double slit experiment all fringes are of equal width.
- Reason (R): The fringe width depends upon the wavelength of light (λ) used, the distance of the screen from the plane of slits (D) and slits separation (d).
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is NOT the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Assertion (A) is true and Reason (R) is false.
Assertion (A) is false and Reason (R) is also false.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
In Young's double-slit experiment, the separation between the two slits is d and the distance of the screen from the slits is 1000 d. If the first minima fall at a distance d from the central maximum, obtain the relation between d and λ.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
How are infrared waves produced?
Chapter: [0.08] Electromagnetic Waves
Why are infra-red waves often called heat waves? Explain.
Chapter: [0.08] Electromagnetic Waves
Give any two uses of infrared waves.
Chapter: [0.08] Electromagnetic Waves
How are X-rays produced?
Chapter: [0.08] Electromagnetic Waves
Write two uses of the following radiation.
X-rays
Chapter: [0.08] Electromagnetic Waves
In the given figure the radius of curvature of the curved face in the planoconvex and the planoconcave lens is 15 cm each. The refractive index of the material of the lenses is 1.5. Find the final position of the image formed.
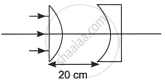
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Advertisements
What happens to the interference pattern when two coherent sources are infinitely close?
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
What happens to the interference pattern when two coherent sources are far apart from each other?
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
What is meant by ionisation energy?
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
Write the ionisation energy value for the hydrogen atom.
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
How mass defect is related to the stability of the nucleus?
Chapter: [0.13] Nuclei
Draw an energy band diagram for an n-type semiconductor at T > 0 K.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Draw an energy band diagram for a p-type semiconductor at T > 0 K.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
A point object in the air is placed symmetrically at a distance of 60 cm in front of a concave spherical surface with a refractive index of 1.5. If the radius of curvature of the surface is 20 cm, find the position of the image formed.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
A series RL circuit with R = 10 Ω and L = `(100/pi)` mH is connected to an ac source of voltage V = 141 sin (100 πt), where V is in volts and t is in seconds. Calculate
- the impedance of the circuit
- phase angle, and
- the voltage drop across the inductor.
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
A ray of light is incident on a glass prism of refractive index µ and refracting angle A. If it just suffers total internal reflection at the other face, obtain a relation between the angle of incidence, angle of prism and critical angle.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
A series CR circuit with R = 200 Ω and C = (50/π) µF is connected across an ac source of peak voltage ε0 = 100 V and frequency v = 50 Hz. Calculate (a) impedance of the circuit (Z), (b) phase angle (Φ), and (c) voltage across the resistor.
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
Two cells of emf E1 and E2 and internal resistances r1 and r2 are connected in parallel, with their terminals of the same polarity connected together. Obtain an expression for the equivalent emf of the combination.
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Distinguish between nuclear fission and fusion giving an example of each.
Chapter: [0.13] Nuclei
Explain the release of energy in nuclear fission and fusion on the basis of binding energy per nucleon curve.
Chapter: [0.13] Nuclei
How is the size of a nucleus found experimentally? Write the relation between the radius and mass number of a nucleus.
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
Answer the following question.
Show that the density of the nucleus is independent of its mass number A.
Chapter: [0.13] Nuclei
Use Gauss' law to derive the expression for the electric field `(vecE)` due to a straight uniformly charged infinite line of charge density λ C/m.
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
An infinitely long positively charged straight wire has a linear charge density λ. An electron is revolving in a circle with a constant speed v such that the wire passes through the centre, and is perpendicular to the plane, of the circle. Find the kinetic energy of the electron in terms of the magnitudes of its charge and linear charge density λ on the wire.
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
Draw a graph of kinetic energy as a function of linear charge density λ.
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
Advertisements
Consider two identical point charges located at points (0, 0) and (a, 0).
Is there a point on the line joining them at which the electric field is zero?
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
Consider two identical point charges located at points (0, 0) and (a, 0).
Is there a point on the line joining them at which the electric potential is zero?
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
Justify your answers for each case.
State the significance of the negative value of electrostatic potential energy of a system of charges.
Three charges are placed at the corners of an equilateral triangle ABC of side 2.0 m as shown in the figure. Calculate the electric potential energy of the system of three charges.
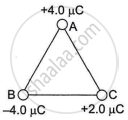
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Define the coefficient of self-induction.
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
Derive the expression for the self-inductance of a long solenoid of cross sectional area A and length l, having n turns per unit length.
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
Calculate the self-inductance of a coil using the following data obtained when an AC source of frequency `(200/pi)` Hz and a DC source are applied across the coil.
| AC Source | ||
| S.No. | V (volts) | I (A) |
| 1 | 3.0 | 0.5 |
| 2 | 6.0 | 1.0 |
| 3 | 9.0 | 1.5 |
| DC Source | ||
| S.No. | V (volts) | I (A) |
| 1 | 4.0 | 1.0 |
| 2 | 6.0 | 1.5 |
| 3 | 8.0 | 2.0 |
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
With the help of a labelled diagram, describe the principle and working of an ac generator. Hence, obtain an expression for the instantaneous value of the emf generated.
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
The coil of an ac generator consists of 100 turns of wire, each of area 0.5 m2. The resistance of the wire is 100 Ω. The coil is rotating in a magnetic field of 0.8 T perpendicular to its axis of rotation, at a constant angular speed of 60 radians per second. Calculate the maximum emf generated and power dissipated in the coil.
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
With the help of a diagram, show how a plane wave is reflected from a surface. Hence verify the law of reflection.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
A concave mirror of focal length 12 cm forms three times the magnified virtual image of an object. Find the distance of the object from the mirror.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Draw a labelled ray diagram showing the image formation by a refracting telescope. Define its magnifying power.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Write two important limitations of a refracting telescope over a reflecting-type telescope.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
The focal lengths of the objective and the eye-piece of a compound microscope are 1.0 cm and 2.5 cm respectively. Find the tube length of the microscope for obtaining a magnification of 300.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Read the following paragraph and answer the questions.
|
Consider the experimental set-up shown in the figure. This jumping ring experiment is an outstanding demonstration of some simple laws of Physics. A conducting non-magnetic ring is placed over the vertical core of a solenoid. When current is passed through the solenoid, the ring is thrown off. |
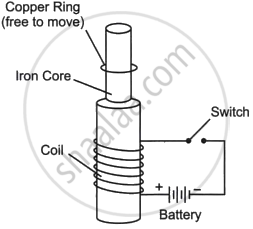
- Explain the reason for the jumping of the ring when the switch is closed in the circuit.
- What will happen if the terminals of the battery are reversed and the switch is closed? Explain.
- Explain the two laws that help us understand this phenomenon.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Briefly explain various ways to increase the strength of the magnetic field produced by a given solenoid.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Read the following paragraph and answer the questions.
| The figure shows the variation of photoelectric current measured in a photocell circuit as a function of the potential difference between the plates of the photocell when light beams A, B, C and D of different wavelengths are incident on the photocell. Examine the given figure and answer the following questions: |
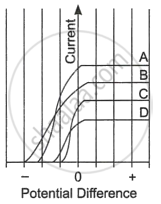
- Which light beam has the highest frequency and why?
- Which light beam has the longest wavelength and why?
- Which light beam ejects photoelectrons with maximum momentum and why?
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
What is the effect of threshold frequency and stopping potential on increasing the frequency of the incident beam of light? Justify your answer.
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 12 Physics with solutions 2022 - 2023
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 12 Physics-2023 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Physics, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 12.
How CBSE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Physics will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
