Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Read the following paragraph and answer the questions.
| The figure shows the variation of photoelectric current measured in a photocell circuit as a function of the potential difference between the plates of the photocell when light beams A, B, C and D of different wavelengths are incident on the photocell. Examine the given figure and answer the following questions: |
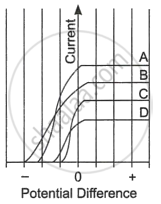
- Which light beam has the highest frequency and why?
- Which light beam has the longest wavelength and why?
- Which light beam ejects photoelectrons with maximum momentum and why?
Solution
(i) We know that the stopping potential and frequency are related as
V = `((hf - phi))/q`
Where Φ is the work function defined as the amount of energy needed to bind the electrons in the metals, hf is the energy of photons, and q is the charge.
This relationship leads us to the conclusion that the greater negative the stopping potential, the higher the frequency. As a result, curve B has the highest frequency and the largest negative stopping potential in the graph.
(ii) We all know that the connection between wavelength and frequency is inverse. The wavelength reduces as the frequency rises and vice versa.
As can be seen from the graph, C has the lowest frequency out of all the possible values since its stopping potential is the least negative. Therefore, the wavelength is largest when the frequency is lowest. C has the longest wavelength as a result.
(iii) Highest momentum means highest kinetic energy which can be calculated with the help of velocity.
kinetic energy = `1/2mv^2`
Relation to the momentum, p2 = 2m(K.E.)
If kinetic energy is maximum, then momentum will be maximum.
We know that the stopping potential and frequency are related,
Vq = (hf - Φ)
The maximum kinetic energy of the electrons equals the stopping voltage when measured in electron volt. We can consider Φ as the kinetic energy.
Kinetic energy is maximum when the frequency is maximum and in the above part we have seen that it is maximum for curve B, so momentum is maximum for curve B.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Ultraviolet light of wavelength 2271 Å from a 100 W mercury source irradiates a photo-cell made of molybdenum metal. If the stopping potential is −1.3 V, estimate the work function of the metal. How would the photo-cell respond to a high intensity (∼105 W m−2) red light of wavelength 6328 Å produced by a He-Ne laser?
Monochromatic radiation of wavelength 640.2 nm (1 nm = 10−9 m) from a neon lamp irradiates photosensitive material made of caesium on tungsten. The stopping voltage is measured to be 0.54 V. The source is replaced by an iron source and its 427.2 nm line irradiates the same photo-cell. Predict the new stopping voltage.
The threshold wavelength of a metal is λ0. Light of wavelength slightly less than λ0 is incident on an insulated plate made of this metal. It is found that photoelectrons are emitted for some time and after that the emission stops. Explain.
When the intensity of a light source in increased,
(a) the number of photons emitted by the source in unit time increases
(b) the total energy of the photons emitted per unit time increases
(c) more energetic photons are emitted
(d) faster photons are emitted
An atom absorbs a photon of wavelength 500 nm and emits another photon of wavelength 700 nm. Find the net energy absorbed by the atom in the process.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
A totally reflecting, small plane mirror placed horizontally faces a parallel beam of light, as shown in the figure. The mass of the mirror is 20 g. Assume that there is no absorption in the lens and that 30% of the light emitted by the source goes through the lens. Find the power of the source needed to support the weight of the mirror.
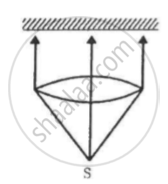
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
Find the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons ejected when light of wavelength 350 nm is incident on a cesium surface. Work function of cesium = 1.9 eV
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
In an experiment on photoelectric effect, the stopping potential is measured for monochromatic light beams corresponding to different wavelengths. The data collected are as follows:-
Wavelength (nm): 350 400 450 500 550
Stopping potential (V): 1.45 1.00 0.66 0.38 0.16
Plot the stopping potential against inverse of wavelength (1/λ) on a graph paper and find (a) Planck's constant (b) the work function of the emitter and (c) the threshold wavelength.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
Define the term: stopping potential in the photoelectric effect.
A metallic plate exposed to white light emits electrons. For which of the following colours of light, the stopping potential will be maximum?
