Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
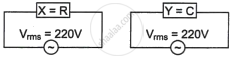
An alternating voltage of 220 V is applied across a device X. A current of 0.22 A flows in the circuit and it lags behind the applied voltage in phase by π/2 radian. When the same voltage is applied across another device Y, the current in the circuit remains the same and it is in phase with the applied voltage.
- Name the devices X and Y and,
- Calculate the current flowing in the circuit when the same voltage is applied across the series combination of X and Y.
Solution
- X is a resistor and Y is the capacitor.
R = `V_{rms}/I_{rms} = 220/0.22 = 1000 Omega`
R = XC = 1000Ω
When R and C are in series.
`I_{rms} = V_{rms}/Z = V_{rms}/sqrt(R^2 + (X_C)^2)`
= `220/sqrt((1000)^2 + (1000)^2)`
= `220/(1000 xx sqrt2)`
`I_{rms} = 0.156` A
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Why does current in a steady state not flow in a capacitor connected across a battery? However momentary current does flow during charging or discharging of the capacitor. Explain.
A source of ac voltage v = v0 sin ωt, is connected across a pure inductor of inductance L. Derive the expressions for the instantaneous current in the circuit. Show that average power dissipated in the circuit is zero.
In a series LCR circuit, obtain the condition under which the impedance of the circuit is minimum ?
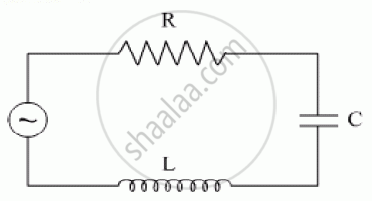
The figure shows a series LCR circuit with L = 10.0 H, C = 40 μF, R = 60 Ω connected to a variable frequency 240 V source, calculate
(i) the angular frequency of the source which drives the circuit at resonance,
(ii) the current at the resonating frequency,
(iii) the rms potential drop across the inductor at resonance.
The potential difference across the resistor is 160V and that across the inductor is 120V. Find the effective value of the applied voltage. If the effective current in the circuit be 1.0 A, calculate the total impedance of the circuit.
A series LCR circuit with R = 20 Ω, L = 1.5 H and C = 35 µF is connected to a variable-frequency 200 V ac supply. When the frequency of the supply equals the natural frequency of the circuit, what is the average power transferred to the circuit in one complete cycle?
Consider the LCR circuit shown in figure. Find the net current i and the phase of i. Show that i = v/Z`. Find the impedance Z for this circuit.
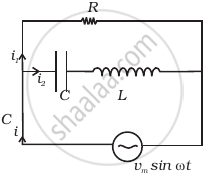
For an LCR circuit driven at frequency ω, the equation reads
`L (di)/(dt) + Ri + q/C = v_i = v_m` sin ωt
- Multiply the equation by i and simplify where possible.
- Interpret each term physically.
- Cast the equation in the form of a conservation of energy statement.
- Integrate the equation over one cycle to find that the phase difference between v and i must be acute.
Define Impedance.
When an alternating voltage of 220V is applied across device X, a current of 0.25A flows which lags behind the applied voltage in phase by π/2 radian. If the same voltage is applied across another device Y, the same current flows but now it is in phase with the applied voltage.
- Name the devices X and Y.
- Calculate the current flowing in the circuit when the same voltage is applied across the series combination of X and Y.
