Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
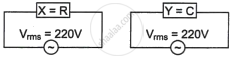
An alternating voltage of 220 V is applied across a device X. A current of 0.22 A flows in the circuit and it lags behind the applied voltage in phase by π/2 radian. When the same voltage is applied across another device Y, the current in the circuit remains the same and it is in phase with the applied voltage.
- Name the devices X and Y and,
- Calculate the current flowing in the circuit when the same voltage is applied across the series combination of X and Y.
उत्तर
- X is a resistor and Y is the capacitor.
R = `V_{rms}/I_{rms} = 220/0.22 = 1000 Omega`
R = XC = 1000Ω
When R and C are in series.
`I_{rms} = V_{rms}/Z = V_{rms}/sqrt(R^2 + (X_C)^2)`
= `220/sqrt((1000)^2 + (1000)^2)`
= `220/(1000 xx sqrt2)`
`I_{rms} = 0.156` A
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
(i) Find the value of the phase difference between the current and the voltage in the series LCR circuit shown below. Which one leads in phase : current or voltage ?
(ii) Without making any other change, find the value of the additional capacitor C1, to be connected in parallel with the capacitor C, in order to make the power factor of the circuit unity.
A source of ac voltage v = v0 sin ωt, is connected across a pure inductor of inductance L. Derive the expressions for the instantaneous current in the circuit. Show that average power dissipated in the circuit is zero.
An LR circuit with emf ε is connected at t = 0. (a) Find the charge Q which flows through the battery during 0 to t. (b) Calculate the work done by the battery during this period. (c) Find the heat developed during this period. (d) Find the magnetic field energy stored in the circuit at time t. (e) Verify that the results in the three parts above are consistent with energy conservation.
An ac circuit as shown in the figure has an inductor of inductance L and a resistor or resistance R connected in series. Using the phasor diagram, explain why the voltage in the circuit will lead the current in phase.
At resonant frequency the current amplitude in series LCR circuit is ______.
To reduce the resonant frequency in an LCR series circuit with a generator
A coil of 0.01 henry inductance and 1 ohm resistance is connected to 200 volt, 50 Hz ac supply. Find the impedance of the circuit and time lag between max. alternating voltage and current.
For an LCR circuit driven at frequency ω, the equation reads
`L (di)/(dt) + Ri + q/C = v_i = v_m` sin ωt
- Multiply the equation by i and simplify where possible.
- Interpret each term physically.
- Cast the equation in the form of a conservation of energy statement.
- Integrate the equation over one cycle to find that the phase difference between v and i must be acute.
A series LCR circuit containing a resistance of 120 Ω has angular resonance frequency 4 × 105 rad s-1. At resonance the voltage across resistance and inductance are 60 V and 40 V respectively. At what frequency the current in the circuit lags the voltage by 45°. Give answer in ______ × 105 rad s-1.
A series LCR circuit is connected to an ac source. Using the phasor diagram, derive the expression for the impedance of the circuit.
