Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
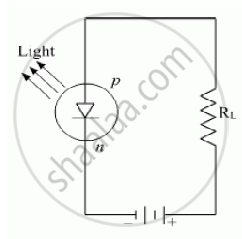
How does a light emitting diode (LED) work? Give two advantages of LED’s over the conventional incandescent lamps.
Solution
When we apply sufficient voltage to LED, electron move across the junction into the p-region and get attracted to the holes there. Thus, electrons and holes recombine. During each recombination, electric potential energy is converted into electromagnetic energy and a photon of light with a characteristic frequency is emitted, this is how LED works.
Advantage of LEDs over incandescent lamps
(1) Since LEDs do not have a filament that can burn out, they last longer.
(2) They do not get hot during use.
RELATED QUESTIONS
Sunil and his parents were travelling to their village in their car. On the way his mother noticed some grey coloured panels installed on the roof of a low building. She enquired from Sunil what those panels were and Sunil told his mother that those were solar panels.
(a) What were the values displayed by Sunil and his mother? State one value for each.
(b) In what way would the use of solar panels prove to be very useful?
(c) Name the semiconductor device used in solar panels. Briefly explain with the help of a diagram, how this device works
The current in the forward bias is known to be more (~mA) than the current in the reverse bias (~μA). What is the reason, then, to operate the photodiode in reverse bias?
Write the important considerations which are to be taken into account while fabricating a p-n junction diode to be used as a Light Emitting Diode (LED). What should be the order of the band gap of an LED, if it is required to emit light in the visible range? Draw a circuit diagram and explain its action.
Answer the following question.
Draw solar cell V-I characteristics.
Explain photodiode.
A p-n photodiode is fabricated from a semiconductor with a band gap of 2.5 eV. lt can detect a signal of wavelength ______.
The amplifiers X, Y and Z are connected in series. If the voltage gains of X, Y and Z are 10, 20 and 30, respectively and the input signal is 1 mV peak value, then what is the output signal voltage (peak value)
- if dc supply voltage is 10V?
- if dc supply voltage is 5V?
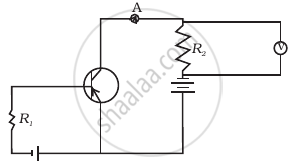
If the resistance R1 is increased (Figure), how will the readings of the ammeter and voltmeter change?
Why a photo-diode is operated in reverse bias whereas the current in the forward bias is much larger than that in the reverse bias? Explain. Mention its two uses.
Draw the circuit diagram of an illuminated photodiode and its I-V characteristics.
