Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How does a light emitting diode (LED) work? Give two advantages of LED’s over the conventional incandescent lamps.
उत्तर
When we apply sufficient voltage to LED, electron move across the junction into the p-region and get attracted to the holes there. Thus, electrons and holes recombine. During each recombination, electric potential energy is converted into electromagnetic energy and a photon of light with a characteristic frequency is emitted, this is how LED works.
Advantage of LEDs over incandescent lamps
(1) Since LEDs do not have a filament that can burn out, they last longer.
(2) They do not get hot during use.
संबंधित प्रश्न
The current in the forward bias is known to be more (~mA) than the current in the reverse bias (~μA). What is the reason, then, to operate the photodiode in reverse bias?
Describe briefly, with the help of a diagram, the role of the two important processes involved in the formation of a p-n junction ?
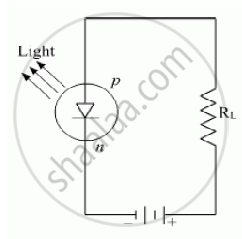
Draw the circuit diagram of an illuminated photodiode in reverse bias. How is photodiode used to measure light intensity?
Answer the following question.
Draw solar cell V-I characteristics.
Answer the following question.
Explain the three processes involved in solar cell working.
Pressure P varies as P = `alpha/beta "exp" (- (alpha x)/"k"_"BT")`, where x denotes the distance, kB is the Boltzmann's constant, T is the absolute temperature and α and β are constant. The dimension of β is ______.
Read the following paragraph and answer the questions.
|
LED is a heavily doped P-N junction which under forward bias emits spontaneous radiation. When it is forward-biased, due to recombination of holes and electrons at the junction, energy is released in the form of photons. In the case of Si and Ge diode, the energy released in recombination lies in the infrared region. LEDs that can emit red, yellow, orange, green and blue light are commercially available. The semiconductor used for fabrication of visible LEDs must at least have a band gap of 1.8 eV. The compound semiconductor Gallium Arsenide – Phosphide is used for making LEDs of different colours.
|
- Why are LEDs made of compound semiconductor and not of elemental semiconductors?
- What should be the order of bandgap of an LED, if it is required to emit light in the visible range?
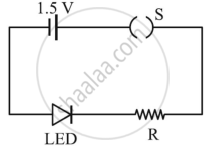
- A student connects the blue coloured LED as shown in the figure. The LED did not glow when switch S is closed. Explain why?
OR
iii. Draw V-I characteristic of a p-n junction diode in
(i) forward bias and (ii) reverse bias
Draw the circuit diagram of an illuminated photodiode and its I-V characteristics.
How can a photodiode be used to measure light intensity?
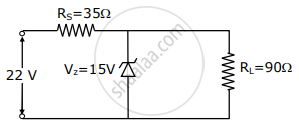
The value of power dissipated across the Zener diode (Vz = 15 V) connected in the circuit as shown in the figure is x × 10–1 watt. The value of x, to the nearest integer, is ______.