Science (English Medium)
Academic Year: 2011-2012
Date: March 2012
Advertisements
Why is the potential inside a hollow spherical charged conductor constant and has the same value of as on its surface?
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
A magnetic needle, free to rotate in a vertical plane, orients itself vertically at a certain place on the Earth. What are the values of (i) Horizontal component of Earth’s magnetic field and (ii) angle of dip at this place?
Chapter: [0.05] Magnetism and Matter
The closed loop (PQRS) of wire is moved into a uniform magnetic field at right angles to the plane of the paper as shown in the figure, Predict the direction of the induced current in the loop.
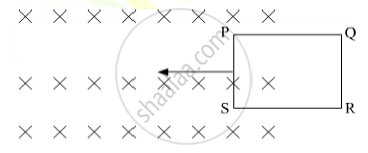
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
Name the electromagnetic waves which (i) maintain the Earth’s warmth and (ii) are used in aircraft navigation.
Chapter: [0.05] Magnetism and Matter
How does focal length of a lens change when red light incident on it is replaced by violet light? Give reason for your answer.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Write the relationship between the size of a nucleus and its mass number (A)?
Chapter: [0.13] Nuclei
Show on a graph the variation of the de Broglie wavelength (λ) associated with an electron, with the square root of accelerating potential (V) ?
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Define dipole moment of an electric dipole. Is it a scalar or a vector?
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
A conductor of length ‘l’ is connected to a dc source of potential ‘V’. If the length of the conductor is tripled by gradually stretching it, keeping ‘V’ constant, how will (i) drift speed of electrons and (ii) resistance of the conductor be affected? Justify your answer.
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Two students ‘X’ and ‘Y’ perform an experiment on potentiometer separately using the circuit given below:
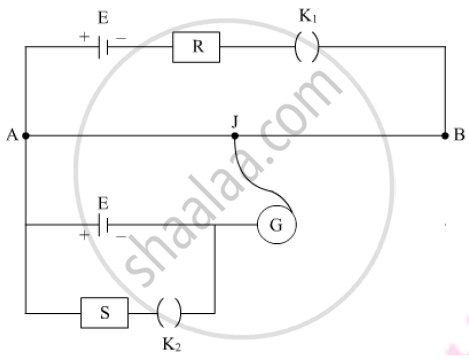
Keeping other parameters unchanged, how will the position of the null point be affected if
(i) ‘X’ increases the value of resistance R in the set-up by keeping the key K1 closed and the Key K2 opens?
(ii) ‘Y’ decreases the value of resistance S in the set-up, while the key K2 remains open and they K1 closed?
Justify.
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
A particle of charge ‘q’ and mass ‘m’ is moving with velocity .`vecV` It is subjected to a uniform magnetic field `vecB` directed perpendicular to its velocity. Show that it describes a circular path. Write the expression for its radius.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Calculate the quality factor of a series LCR circuit with L = 2.0 H, C = 2μF and R = 10 Ω. Mention the significance of quality factor in LCR circuit.
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
Explain briefly how electromagnetic waves are produced by an oscillating charge. How is the frequency of the em waves produced related to that of the oscillating charge?
Chapter: [0.08] Electromagnetic Waves
In a given sample, two radioisotopes, A and B, are initially present in the ration of 1 : 4. The half lives of A and B are respectively 100 years and 50 years. Find the time after which the amounts of A and B become equal.
Chapter: [0.13] Nuclei
Figure shows a block diagram of a transmitter identify the boxes ‘X’ and ‘Y’ and write their functions.
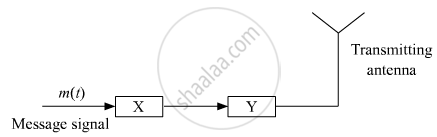
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Trace the path of a ray of light passing through a glass prism (ABC) as shown in the figure. If the refractive index of glass is `sqrt3`, find out the value of the angle of emergence from the prism.
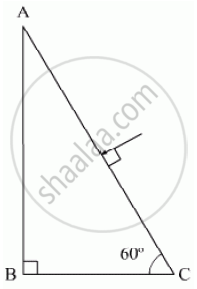
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Advertisements
Write two characteristic features to distinguish between n-type and p-type semiconductors ?
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
How does a light emitting diode (LED) work? Give two advantages of LED’s over the conventional incandescent lamps.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
A short bar magnet of magnetic moment 0.9 J/T is placed with its axis at 30° to a uniform magnetic field. It experiences a torque of 0.063 J.
(i) Calculate the magnitude of the magnetic field.
(ii) In which orientation will the bar magnet be in stable equilibrium in the magnetic field?
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
State Gauss’s law in electrostatics. A cube which each side ‘a’ is kept is an electric field given by `vecE` = C × l. (as is shown in the figure where C is a positive dimensional constant. Find out
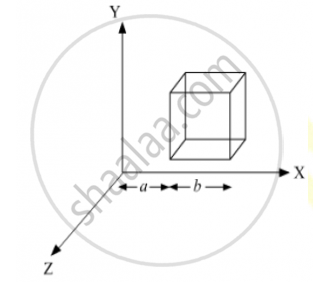
(i) The electric flux through the cube, and
(ii) The net charge inside the cube.
Chapter: [0.05] Magnetism and Matter
A capacitor of 200 pF is charged by a 300 V battery. The battery is then disconnected and the charge capacitor is connected to another uncharged capacitor of 100 pF. Calculate the difference between the final energy stored in the combined system and the initial energy stored in the single capacitor.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Draw a labelled diagram of a moving coil galvanometer and explain its working. What is the function of radial magnetic field inside the coil?
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Define power of a lens. Write its units. Deduce the relation `1/f =1/f_1 +1/f_2`for two thin lenses kept in contact coaxially.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Write two characteristic features observed is photoelectric effect which supports the photon pictures of electromagnetic radiation ?
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Draw a graph between the frequency of incident radiation (υ) and the maximum kinetic energy of the electrons emitted from the surface of a photosensitive material state clearly how this graph can be used to determine (i) Planck’s constant and (ii) work function of the material.
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Define modulation index.
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
Given modulation index physical significance .For an amplitude modulated wave, the maximum amplitude is found to be 10 V while the minimum amplitude is 2 V. Determine the modulation index μ ?
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
Two cells of emf E1, E2 and internal resistance r1 and r2 respectively are connected in parallel as shown in the figure.

Deduce the expressions for
(1) the equivalent e.m.f of the combination
(2) the equivalent resistance of the combination, and
(3) the potential difference between the point A and B.
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Using Bohr’s postulates for hydrogen atom, show that the total energy (E) of the electron in the stationary states tan be expressed as the sum of kinetic energy (K) and potential energy (U), where K = −2U. Hence deduce the expression for the total energy in the nth energy level of hydrogen atom.
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
Use Huygens’ geometrical construction to show the propagation of plane wavefront a rarer medium (1) to a denser medium (2) undergoing refraction.
Hence derive Snell’s law of refraction.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Use Huygens’ geometrical construction to show the behavior of a plane wavefront.
(i) Passing through a biconvex lens;
(ii) Reflecting by a concave mirror
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
When monochromatic light is incident on a surface separating two media, why does the refracted light have the same frequency as that of the incident light?
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Advertisements
What is the effect on the interference fringes to a Young’s double slit experiment when
(i) the separation between the two slits is decreased?
(ii) the width of a source slit is increased?
(iii) the monochromatic source is replaced by a source of white light?
Justify your answer in each case.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
The intensity at the central maxima in Young’s double slit experimental set-up is I0. Show that the intensity at a point where the path difference is λ/3 is I0/4.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Obtain the conditions for the bright and dark fringes in diffraction pattern due to a single narrow slit illuminated by a monochromatic source.
Explain clearly why the secondary maxima go on becoming weaker with increasing.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
When the width of the slit is made double, how would this affect the size and intensity of the central diffraction band? Justify.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
State the principle on which the AC generator works. Draw a labelled diagram and explain its working.
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
A conducting rod held horizontally along East- West direction is dropped from rest from a certain height near the Earth’s surface. Why should there be an induced emf across the end of the rod? Draw a plot showing the instantaneous variation of emf as a function of time from the instant it begins to fall.
Chapter: [0.05] Magnetism and Matter
State the principle of a step-up transformer. Explain, with the help of a labeled diagram, its working ?
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
Describe briefly and two energy losses, giving the reasons for their occurrence in actual transformers ?
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
Draw the circuit for studying the input and output characteristics of and transistor in CE configuration. Show, how, from the output characteristics, the information about the current amplification factor (βac) can obtained.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Draw a plot of the transfer characteristics (V0 versus Vi) for a base-biased transistor in CE configuration. Show for which regions in the plot, the transistor can operate as a switch ?
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Why is a zener diode considered as a special purpose semiconductor diode?
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Draw the I − V characteristics of zener diode and explain briefly how reverse current suddenly increase at the breakdown voltage.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Describe briefly with the help of a circuit diagram how a zener diode works to obtain a constant dc voltage from the unregulated dc output of a rectifier ?
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 12 Physics with solutions 2011 - 2012
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 12 Physics-2012 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Physics, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 12.
How CBSE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Physics will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
