Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Why is the potential inside a hollow spherical charged conductor constant and has the same value of as on its surface?
Solution
Electric field inside the shell is zero. So no work is done in moving a charge inside the shell. This implies that potential is constant, and therefore equal to its value at the surface i.e.
`V=1/(4piE_0) q/r`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
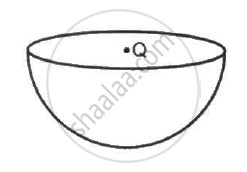
A charge Q is placed at the centre of an imaginary hemispherical surface. Using symmetry arguments and Gauss's Law, find the flux of the electric field due to this charge through the surface of the hemisphere in the following figure.
The radius of a gold nucleus (Z = 79) is about 7.0 × 10-10 m. Assume that the positive charge is distributed uniformly throughout the nuclear volume. Find the strength of the electric field at (a) the surface of the nucleus and (b) at the middle point of a radius. Remembering that gold is a conductor, is it justified to assume that the positive charge is uniformly distributed over the entire volume of the nucleus and does not come to the outer surface?
Consider the following very rough model of a beryllium atom. The nucleus has four protons and four neutrons confined to a small volume of radius 10−15 m. The two 1 selectrons make a spherical charge cloud at an average distance of 1⋅3 ×10−11 m from the nucleus, whereas the two 2 s electrons make another spherical cloud at an average distance of 5⋅2 × 10−11 m from the nucleus. Find three electric fields at (a) a point just inside the 1 s cloud and (b) a point just inside the 2 s cloud.
A long cylindrical wire carries a positive charge of linear density 2.0 × 10-8 C m -1 An electron revolves around it in a circular path under the influence of the attractive electrostatic force. Find the kinetic energy of the electron. Note that it is independent of the radius.
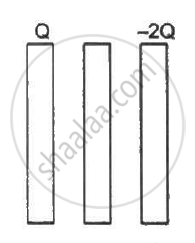
Three identical metal plates with large surface areas are kept parallel to each other as shown in the following figure. The leftmost plate is given a charge Q, the rightmost a charge −2Q and the middle one is kept neutral. Find the charge appearing on the outer surface of the rightmost plate.
A uniform electric field of 10 N C−1 exists in the vertically downward direction. Find the increase in the electric potential as one goes up through a height of 50 cm.
A simple pendulum consists of a small sphere of mass m suspended by a thread of length l. The sphere carries a positive charge q. The pendulum is placed in a uniform electric field of strength E directed vertically downwards. Find the period of oscillation of the pendulum due to the electrostatic force acting on the sphere, neglecting the effect of the gravitational force.
When a comb rubbed with dry hair attracts pieces of paper. This is because the ______.
Pick out the statement which is incorrect
