Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Why is the potential inside a hollow spherical charged conductor constant and has the same value of as on its surface?
उत्तर
Electric field inside the shell is zero. So no work is done in moving a charge inside the shell. This implies that potential is constant, and therefore equal to its value at the surface i.e.
`V=1/(4piE_0) q/r`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Two identical circular loops 1 and 2 of radius R each have linear charge densities −λ and +λ C/m respectively. The loops are placed coaxially with their centres `Rsqrt3` distance apart. Find the magnitude and direction of the net electric field at the centre of loop 1.
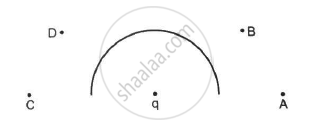
In the following figure shows a charge q placed at the centre of a hemisphere. A second charge Q is placed at one of the positions A, B, C and D. In which position(s) of this second charge, the flux of the electric field through the hemisphere remains unchanged?
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
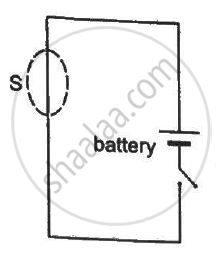
A closed surface S is constructed around a conducting wire connected to a battery and a switch in the following figure. As the switch is closed, the free electrons in the wire start moving along the wire. In any time interval, the number of electrons entering the closed surface S is equal to the number of electrons leaving it. On closing the switch, the flux of the electric field through the closed surface
(a) is increased
(b) is decreased
(c) remains unchanged
(d) remains zero
A charge Q is uniformly distributed over a rod of length l. Consider a hypothetical cube of edge l with the centre of the cube at one end of the rod. Find the minimum possible flux of the electric field through the entire surface of the cube.
The radius of a gold nucleus (Z = 79) is about 7.0 × 10-10 m. Assume that the positive charge is distributed uniformly throughout the nuclear volume. Find the strength of the electric field at (a) the surface of the nucleus and (b) at the middle point of a radius. Remembering that gold is a conductor, is it justified to assume that the positive charge is uniformly distributed over the entire volume of the nucleus and does not come to the outer surface?
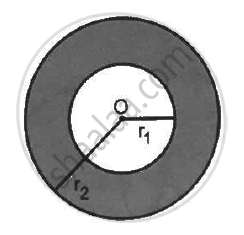
A charge Q is distributed uniformly within the material of a hollow sphere of inner and outer radii r1 and r2 (see the figure). Find the electric field at a point P at a distance x away from the centre for r1 < x < r. Draw a rough graph showing the electric field as a function of x for 0 < x < 2r2 (see the figure).
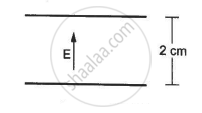
An electric field of magnitude 1000 NC−1 is produced between two parallel plates with a separation of 2.0 cm, as shown in the figure. (a) What is the potential difference between the plates? (b) With what minimum speed should an electron be projected from the lower place in the direction of the field, so that it may reach the upper plate? (c) Suppose the electron is projected from the lower place with the speed calculated in part (b). The direction of projection makes an angle of 60° with the field. Find the maximum height reached by the electron.
A simple pendulum consists of a small sphere of mass m suspended by a thread of length l. The sphere carries a positive charge q. The pendulum is placed in a uniform electric field of strength E directed vertically downwards. Find the period of oscillation of the pendulum due to the electrostatic force acting on the sphere, neglecting the effect of the gravitational force.
When a comb rubbed with dry hair attracts pieces of paper. This is because the ______.
