Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
State Huygen’s principle. Using this principle explain how a diffraction pattern is obtained on a screen due to a narrow slit on which a narrow beam coming from a `=> n = (vlamda)/(vlamda_omega)`monochromatic source of light is incident normally.
Solution
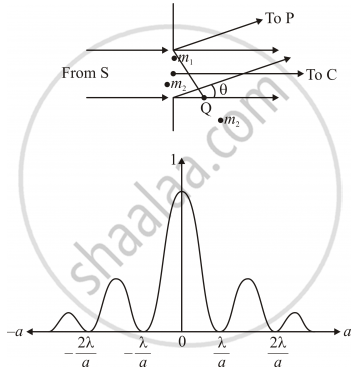
Huygen’s Principle
It states that
(i) Rays (light rays) are perpendicular to wave fronts.
Where wave fronts are defined as a surface of constant phase.
(ii) The time taken for light to travel from one wave front to another is same along any ray.
Diffraction Pattern:
Explanation of diffraction phenomena along with the following diagrams.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
When monochromatic light is incident on a surface separating two media, the reflected and refracted light both have the same frequency as the incident frequency.
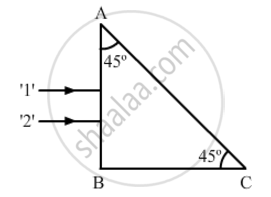
Two monochromatic rays of light are incident normally on the face AB of an isosceles right-angled prism ABC. The refractive indices of the glass prism for the two rays '1' and '2' are respectively 1.35 and 1.45. Trace the path of these rays after entering the prism.
When light travels from a rarer to a denser medium, the speed decreases. Does this decrease in speed imply a reduction in the energy carried by the wave?
A monochromatic ray of light falls on a regular prism. What is the relation between the angle of incidence and angle of emergence in the case of minimum deviation?
State the essential conditions for diffraction of light ?
When monochromatic light travels from a rarer to a denser medium, explain the following, giving reasons:
(i) Is the frequency of reflected and refracted light same as the frequency of incident light?
(ii) Does the decrease in speed imply a reduction in the energy carried by light wave?
When monochromatic light is incident on a surface separating two media, why does the refracted light have the same frequency as that of the incident light?
Which of the following sources provides the best monochromatic light?
Find the angle of incidence at which a ray of monochromatic light should be incident on the first surface AB of a regular glass prism ABC so that the emergent ray grazes the adjacent surface AC. (Refractive Index of glass = 1 .56)
Assertion(A): The photoelectrons produced by a monochromatic light beam incident on a metal surface have a spread in their kinetic energies.
Reason(R): The energy of electrons emitted from inside the metal surface, is lost in collision with the other atoms in the metal.
