HSC Science (General)
HSC Science (Electronics)
HSC Science (Computer Science)
Academic Year: 2013-2014
Date: March 2014
Advertisements
Explain the rise of liquid in the capillary on the basis of pressure difference.
Chapter: [0.02] Mechanical Properties of Fluids [0.06] Surface Tension
Show graphical representation of energy distribution spectrum of perfectly black body.
Chapter: [0.09] Kinetic Theory of Gases and Radiation
The escape velocity of a body from the surface of the earth is 11.2 km/s. If a satellite were to orbit close to the surface, what would be its critical velocity?
Chapter: [0.02] Gravitation
A pipe which is open at both ends is 47 cm long and has an inner diameter 5 cm. If the speed of sound in air is 348 m/s, calculate the fundamental frequency of air column in that pipe.
Chapter: [0.06] Superposition of Waves [0.08] Stationary Waves
Show that R.M.S. velocity of gas molecules is directly proportional to square root of its absolute temperature.
Chapter: [0.09] Kinetic Theory of Gases and Radiation
For a particle performing uniform circular motion `vecv=vecomegaxxvecr`obtain an expression for linear acceleration of the particle performing non-uniform circular motion.
Chapter: [0.01] Circular Motion
A stone of mass 1 kg is whirled in horizontal circle attached at the end of a 1 m long string. If the string makes an angle of 30º with vertical, calculate the centripetal force acting on the stone.(g=9.8m/s2).
Chapter: [0.01] Circular Motion
A solid cylinder of uniform density of radius 2 cm has mass of 50 g. If its length is 12 cm, calculate its moment of inertia about an axis passing through its centre and perpendicular to its length.
Chapter: [0.03] Angular Momentum
Derive an expression for acceleration due to gravity at depth ‘d’ below the earth’s surface.
Chapter: [0.02] Gravitation
A copper metal cube has each side of length 1 m. The bottom edge of the cube is fixed and tangential force 4.2x108 N is applied to a top surface. Calculate the lateral displacement of the top surface if modulus of rigidity of copper is 14x1010 N/m2.
Chapter: [0.04] Oscillations [0.05] Oscillations
State an expression for K. E. (kinetic energy) and P. E. (potential energy) at displacement ‘x’ for a particle performing linear S.H. M. Represent them graphically. Find the displacement at which K. E. is equal to P. E.
Chapter: [0.04] Oscillations
The equation of simple harmonic progressive wave is given by `y=0.05sinpi[20t-x/6]` where all quantities are in S. I. units. Calculate the displacement of a particle at 5 m from origin and at the instant 0.1 second.
Chapter: [0.07] Wave Motion
State the theorem of parallel axes about moment of inertia.
Chapter: [0.03] Angular Momentum
Prove the theorem of parallel axes about moment of inertia
Chapter: [0.01] Rotational Dynamics [0.03] Angular Momentum
Calculate the density of paraffin oil, if glass capillary of diameter 0.25 mm dipped in paraffin oil of surface tension 0.0245 N/m rises to a height of 4 cm. (Angle of contact of paraffin with glass = 28° and acceleration due to gravity = 9.8 m/s2.)
Chapter: [0.02] Mechanical Properties of Fluids [0.06] Surface Tension
Advertisements
A wire of density ‘ρ’ and Young’s modulus ‘Y’ is stretched between two rigid supports separated by a distance ‘L’ under tension ‘T’. Derive an expression for its frequency in fundamental mode. Hence show that `n=1/(2L)sqrt((Yl)/(rhoL))` where symbols have their usual meanings
Chapter: [0.07] Wave Motion
When the length of a simple pendulum is decreased by 20 cm, the period changes by 10%. Find the original length of the pendulum.
Chapter: [0.04] Oscillations
The bulging of earth at the equator and flattening at the poles is due to _______.
Centripetal Force
Centrifugal Force
Gravitational Force
Electrostatic Force
Chapter: [0.01] Circular Motion
Young’s modulus of material of wire is ‘Y’ and strain energy per unit volume is ‘E’, then the strain is
(A) `sqrtY/(2E)`
(B) `sqrt(E/Y)`
(C) `sqrt((2E)/Y)`
(D) `sqrt(2EY)`
Chapter: [0.05] Elasticity
The wavelength range of thermal radiation is
(A) from 4000 Å to 7000 Å
(B) from 7700 Å to 4 x 106 Å
(C) from 106 Å to 108 Å
(D) from 4 x 10-12 Å to 4 x 108 Å
Chapter: [0.09] Kinetic Theory of Gases and Radiation
A pipe open at both ends resonates to a frequency ‘n1’ and a pipe closed at one end resonates to a frequency ‘n2’. If they are joined to form a pipe closed at one end, then the fundamental frequency will be ______.
(A) `(n_1n_2)/(2n_2+n_1)`
(B) `(2n_2n_1)/(2n_2+n_1)`
(C) `(2n_2n_1)/(n_1+n_2)`
(D) `(n_2+2n_1)/(n_1n_2)`
Chapter: [0.06] Superposition of Waves [0.08] Stationary Waves
The phase difference between displacement and acceleration of a particle performing S.H.M. is _______.
(A) `pi/2rad`
(B) π rad
(C) 2π rad
(D)`(3pi)/2rad`
Chapter: [0.04] Oscillations
Let n1 and n2 be the two slightly different frequencies of two sound waves. The time interval between waxing and immediate next waning is ______.
(A) `1/(n_1-n_2)`
(B) `2/(n_1-n_2)`
(C) `(n_1-n_2)/2`
(D) `1/(2(n_1-n_2))`
Chapter: [0.07] Wave Motion
A metal ball cools from 64 °C to 50 °C in 10 minutes and to 42 °C in next 10 minutes. The ratio of rates of fall of temperature during the two intervals is _______.
`4/7`
`7/4`
2
2.5
Chapter: [0.09] Kinetic Theory of Gases and Radiation
Show that the orbital magnetic dipole moment of a revolving electron is `(eVr)/2`
Chapter: [0.15] Magnetism
Describe the construction of photoelectric cell.
Chapter: [0.18] Atoms, Molecules and Nuclei
For a glass plate as a polariser with refractive index 1.633, calculate the angle of incidence at which light is polarised.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Theory of Light
The susceptibility of magnesium at 300 K is 2.4 x 10-5. At what temperature will the susceptibility increase to 3.6 x 10-5?
Chapter: [0.09] Kinetic Theory of Gases and Radiation
Draw a neat labelled diagram for Davisson and Germer experiment, for diffraction of electron wave.
Chapter: [0.18] Atoms, Molecules and Nuclei
Write the functions of the following in communication systems:
Transmitter
Chapter: [0.2] Communication Systems
Write the functions of the following in communication systems:
Receiver
Chapter: [0.2] Communication Systems
A metal rod `1/sqrtpi `m long rotates about one of its ends perpendicular to a plane whose magnetic induction is 4 x 10-3 T. Calculate the number of revolutions made by the rod per second if the e.m.f. induced between the ends of the rod is 16 mV.
Chapter: [0.12] Electromagnetic Induction [0.16] Electromagnetic Inductions
Find the wave number of a photon having energy of 2.072 eV
Given : Charge on electron = 1.6 x 10-19 C,
Velocity of light in air = 3 x 108 m/s,
Planck’s constant = 6.63 x 10-34 J-s.
Chapter: [0.17] Electrons and Photons
Advertisements
State Ampere’s circuital law.
Chapter: [0.14] Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
Obtain an expression for magnetic induction along the axis of the toroid.
Chapter: [0.14] Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
Calculate the radius of second Bohr orbit in hydrogen atom from the given data.
Mass of electron = 9.1 x 10-31kg
Charge on the electron = 1.6 x 10-19 C
Planck’s constant = 6.63 x 10-34 J-s.
Permittivity of free space = 8.85 x 10-12 C2/Nm2
Chapter: [0.18] Atoms, Molecules and Nuclei
Explain the working of P-N junction diode in forward and reverse biased mode.
Chapter: [0.19] Semiconductors
A network of four capacitors of 6 μF each is connected to a 240 V supply. Determine the charge on each capacitor.
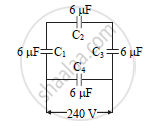
Chapter: [0.12] Electrostatics
Describe biprism experiment to find the wavelength of monochromatic light. Draw the necessary ray diagram for magnified and diminished images of virtual sources.
Chapter: [0.11] Interference and Diffraction
If the difference in velocities of light in glass and water is 2.7 x 107 m/s, find the velocity of light in air. (Refractive index of glass = 1.5, Refractive index of water = 1.333)
Chapter: [0.01] Circular Motion
Explain the construction and working of the transformer.
Chapter: [0.12] Electromagnetic Induction [0.16] Electromagnetic Inductions
State the principle on which transformer works.
Chapter: [0.12] Electromagnetic Induction [0.16] Electromagnetic Inductions
Derive an expression for ratio of e.m.f.s and currents in terms of number of turns in primary and secondary coil.
Chapter: [0.12] Electromagnetic Induction [0.16] Electromagnetic Inductions
Two diametrically opposite points of a metal ring are connected to two terminals of the left gap of meter bridge. The resistance of 11 Ω is connected in right gap. If null point is obtained at a distance of 45 cm from the left end, find the resistance of metal ring.
Chapter: [0.13] Current Electricity
Intensity of electric field at a point close to and outside a charged conducting cylinder is proportional to ______. (r is the distance of a point from the axis of cylinder)
(A) `1/r`
(B) `1/r^2`
(C) `1/r^3`
(D) r3
Chapter: [0.12] Electrostatics
When a hole is produced in P-type semiconductor, there is _______.
extra electron in valence band.
extra electron in conduction band.
missing electron in valence band.
missing electron in conduction band.
Chapter: [0.19] Semiconductors
The outermost layer of the earth’s atmosphere is _______.
(A) stratosphere
(B) mesospher
(C) troposphere
(D) ionosphere
Chapter: [0.2] Communication Systems
Accuracy of potentiometer can be easily increased by ______.
Increasing resistance of wire
Decreasing resistance of wire
Increasing the length of wire
Decreasing the length of wire
Chapter: [0.09] Current Electricity [0.13] Current Electricity
When electron in hydrogen atom jumps from second orbit to first orbit, the wavelength of radiation emitted is λ. When electron jumps from third orbit to first orbit, the wavelength of emitted radiation would be _______.
(A)`27/32lambda`
(B)`32/27lambda`
(C)`2/3lambda`
(D)`3/2lambda`
Chapter: [0.09] Kinetic Theory of Gases and Radiation
An ideal voltmeter has _______.
(A) low resistance
(b) high resistance
(C) infinite resistance
(D) zero resistance
Chapter: [0.09] Current Electricity [0.14] Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
The resolving power of telescope of aperture 100 cm for light of wavelength 5.5 x 10-7 m is _______________.
0.149 x 107
1.49 x 107
14.9 x 107
149 x 107
Chapter: [0.11] Interference and Diffraction
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
Maharashtra State Board previous year question papers 12th Standard Board Exam Physics with solutions 2013 - 2014
Previous year Question paper for Maharashtra State Board 12th Standard Board Exam -2014 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Physics, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of Maharashtra State Board 12th Standard Board Exam.
How Maharashtra State Board 12th Standard Board Exam Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Physics will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
