Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The phase difference between displacement and acceleration of a particle performing S.H.M. is _______.
(A) `pi/2rad`
(B) π rad
(C) 2π rad
(D)`(3pi)/2rad`
Solution
π rad
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
If the metal bob of a simple pendulum is replaced by a wooden bob of the same size, then its time period will.....................
- increase
- remain same
- decrease
- first increase and then decrease.
When the length of a simple pendulum is decreased by 20 cm, the period changes by 10%. Find the original length of the pendulum.
A spring having with a spring constant 1200 N m–1 is mounted on a horizontal table as shown in Fig. A mass of 3 kg is attached to the free end of the spring. The mass is then pulled sideways to a distance of 2.0 cm and released.

Determine (i) the frequency of oscillations, (ii) maximum acceleration of the mass, and (iii) the maximum speed of the mass.
let us take the position of mass when the spring is unstretched as x = 0, and the direction from left to right as the positive direction of the x-axis. Give x as a function of time t for the oscillating mass if at the moment we start the stopwatch (t = 0), the mass is
(a) at the mean position,
(b) at the maximum stretched position, and
(c) at the maximum compressed position.
In what way do these functions for SHM differ from each other, in frequency, in amplitude or the initial phase?
The acceleration due to gravity on the surface of moon is 1.7 ms–2. What is the time period of a simple pendulum on the surface of moon if its time period on the surface of earth is 3.5 s? (g on the surface of earth is 9.8 ms–2)
Answer the following questions:
A man with a wristwatch on his hand falls from the top of a tower. Does the watch give correct time during the free fall?
A simple pendulum of length l and having a bob of mass M is suspended in a car. The car is moving on a circular track of radius R with a uniform speed v. If the pendulum makes small oscillations in a radial direction about its equilibrium position, what will be its time period?
The cylindrical piece of the cork of density of base area A and height h floats in a liquid of density `rho_1`. The cork is depressed slightly and then released. Show that the cork oscillates up and down simple harmonically with a period
`T = 2pi sqrt((hrho)/(rho_1g)`
where ρ is the density of cork. (Ignore damping due to viscosity of the liquid).
Define practical simple pendulum
If the particle starts its motion from mean position, the phase difference between displacement and acceleration is ______.
A simple pendulum has a time period of T1 when on the earth's surface and T2 when taken to a height R above the earth's surface, where R is the radius of the earth. The value of `"T"_2 // "T"_1` is ______.
If the maximum velocity and acceleration of a particle executing SHM are equal in magnitude, the time period will be ______.
A particle executing S.H.M. has a maximum speed of 30 cm/s and a maximum acceleration of 60 cm/s2. The period of oscillation is ______.
Which of the following statements is/are true for a simple harmonic oscillator?
- Force acting is directly proportional to displacement from the mean position and opposite to it.
- Motion is periodic.
- Acceleration of the oscillator is constant.
- The velocity is periodic.
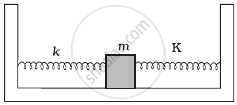
Two identical springs of spring constant K are attached to a block of mass m and to fixed supports as shown in figure. When the mass is displaced from equilibrium position by a distance x towards right, find the restoring force
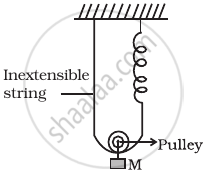
Find the time period of mass M when displaced from its equilibrium position and then released for the system shown in figure.
Consider a pair of identical pendulums, which oscillate with equal amplitude independently such that when one pendulum is at its extreme position making an angle of 2° to the right with the vertical, the other pendulum makes an angle of 1° to the left of the vertical. What is the phase difference between the pendulums?
A tunnel is dug through the centre of the Earth. Show that a body of mass ‘m’ when dropped from rest from one end of the tunnel will execute simple harmonic motion.
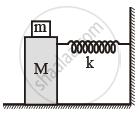
In the given figure, a mass M is attached to a horizontal spring which is fixed on one side to a rigid support. The spring constant of the spring is k. The mass oscillates on a frictionless surface with time period T and amplitude A. When the mass is in equilibrium position, as shown in the figure, another mass m is gently fixed upon it. The new amplitude of oscillation will be:
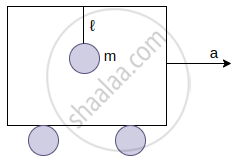
A pendulum of mass m and length ℓ is suspended from the ceiling of a trolley which has a constant acceleration a in the horizontal direction as shown in the figure. Work done by the tension is ______.
(In the frame of the trolley)
A particle at the end of a spring executes simple harmonic motion with a period t1, while the corresponding period for another spring is t2. If the period of oscillation with the two springs in series is T, then ______.
