Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The phase difference between displacement and acceleration of a particle performing S.H.M. is _______.
(A) `pi/2rad`
(B) π rad
(C) 2π rad
(D)`(3pi)/2rad`
उत्तर
π rad
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The period of a conical pendulum in terms of its length (l), semi-vertical angle (θ) and acceleration due to gravity (g) is:
When the length of a simple pendulum is decreased by 20 cm, the period changes by 10%. Find the original length of the pendulum.
The acceleration due to gravity on the surface of moon is 1.7 ms–2. What is the time period of a simple pendulum on the surface of moon if its time period on the surface of earth is 3.5 s? (g on the surface of earth is 9.8 ms–2)
Answer the following questions:
The motion of a simple pendulum is approximately simple harmonic for small angle oscillations. For larger angles of oscillation, a more involved analysis shows that T is greater than `2pisqrt(1/g)` Think of a qualitative argument to appreciate this result.
Answer the following questions:
A man with a wristwatch on his hand falls from the top of a tower. Does the watch give correct time during the free fall?
Answer the following questions:
What is the frequency of oscillation of a simple pendulum mounted in a cabin that is freely falling under gravity?
A simple pendulum of length l and having a bob of mass M is suspended in a car. The car is moving on a circular track of radius R with a uniform speed v. If the pendulum makes small oscillations in a radial direction about its equilibrium position, what will be its time period?
The cylindrical piece of the cork of density of base area A and height h floats in a liquid of density `rho_1`. The cork is depressed slightly and then released. Show that the cork oscillates up and down simple harmonically with a period
`T = 2pi sqrt((hrho)/(rho_1g)`
where ρ is the density of cork. (Ignore damping due to viscosity of the liquid).
A mass attached to a spring is free to oscillate, with angular velocity ω, in a horizontal plane without friction or damping. It is pulled to a distance x0 and pushed towards the centre with a velocity v0 at time t = 0. Determine the amplitude of the resulting oscillations in terms of the parameters ω, x0 and v0. [Hint: Start with the equation x = acos (ωt+θ) and note that the initial velocity is negative.]
Define practical simple pendulum
Show that, under certain conditions, simple pendulum performs the linear simple harmonic motion.
If the particle starts its motion from mean position, the phase difference between displacement and acceleration is ______.
A simple pendulum has a time period of T1 when on the earth's surface and T2 when taken to a height R above the earth's surface, where R is the radius of the earth. The value of `"T"_2 // "T"_1` is ______.
The relation between acceleration and displacement of four particles are given below: Which one of the particles is executing simple harmonic motion?
A particle executing S.H.M. has a maximum speed of 30 cm/s and a maximum acceleration of 60 cm/s2. The period of oscillation is ______.
Which of the following statements is/are true for a simple harmonic oscillator?
- Force acting is directly proportional to displacement from the mean position and opposite to it.
- Motion is periodic.
- Acceleration of the oscillator is constant.
- The velocity is periodic.
When will the motion of a simple pendulum be simple harmonic?
The length of a second’s pendulum on the surface of earth is 1 m. What will be the length of a second’s pendulum on the moon?
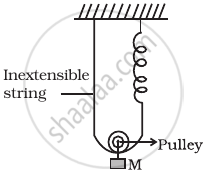
Find the time period of mass M when displaced from its equilibrium position and then released for the system shown in figure.
A body of mass m is situated in a potential field U(x) = U0 (1 – cos αx) when U0 and α are constants. Find the time period of small oscillations.
Consider a pair of identical pendulums, which oscillate with equal amplitude independently such that when one pendulum is at its extreme position making an angle of 2° to the right with the vertical, the other pendulum makes an angle of 1° to the left of the vertical. What is the phase difference between the pendulums?
A tunnel is dug through the centre of the Earth. Show that a body of mass ‘m’ when dropped from rest from one end of the tunnel will execute simple harmonic motion.
