Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A long straight wire in the horizontal plane carries a current of 50 A in north to south direction. Give the magnitude and direction of B at a point 2.5 m east of the wire.
उत्तर
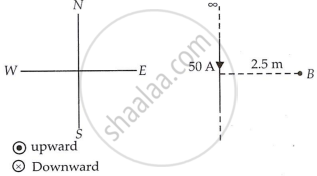
First, let's decide on the standard paper directions.
Magnitude of magnetic field,
`|vecB| = μ_0/(4pi) (2"I")/r`
= `10^-7 xx (2 xx 50)/2.5`
= 40 × 10-7 T
The direction of the magnetic field is upwards when one uses the right hand palm rule.
`vecB = 40 xx 10^-7 hatk`T
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Deduce the expression for the magnetic field at a point on the axis of a current carrying circular loop of radius ‘R’ distant ‘x’ from the centre. Hence, write the magnetic field at the centre of a loop.
A rod of length l is moved horizontally with a uniform velocity 'v' in a direction perpendicular to its length through a region in which a uniform magnetic field is acting vertically downward. Derive the expression for the emf induced across the ends of the rod.
A circular coil of wire consisting of 100 turns, each of radius 8.0 cm carries a current of 0.40 A. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field B at the centre of the coil?
The net charge in a current-carrying wire is zero. Then, why does a magnetic field exert a force on it?
Two wires carrying equal currents i each, are placed perpendicular to each other, just avoiding a contact. If one wire is held fixed and the other is free to move under magnetic forces, what kind of motion will result?
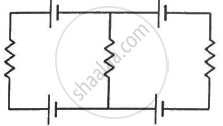
Each of the batteries shown in figure has an emf equal to 5 V. Show that the magnetic field B at the point P is zero for any set of values of the resistances.
Choose the correct alternative and rewrite the following:
What will happen to the current passing through a resistance, if the potential difference across it is doubled and the resistance is halved?
The magnetic moment is NOT associated with ____________.
For a circular coil of radius R and N turns carrying current I, the magnitude of the magnetic field at a point on its axis at a distance x from its centre is given by,
B = `(μ_0"IR"^2"N")/(2("x"^2 + "R"^2)^(3/2))`
(a) Show that this reduces to the familiar result for field at the centre of the coil.
(b) Consider two parallel co-axial circular coils of equal radius R, and number of turns N, carrying equal currents in the same direction, and separated by a distance R. Show that the field on the axis around the mid-point between the coils is uniform over a distance that is small as compared to R, and is given by, B = `0.72 (μ_0"NI")/"R"` approximately.
[Such an arrangement to produce a nearly uniform magnetic field over a small region is known as Helmholtz coils.]
A charged particle enters an environment of a strong and non-uniform magnetic field varying from point to point both in magnitude and direction, and comes out of it following a complicated trajectory. Would its final speed equal the initial speed if it suffered no collisions with the environment?
An electron travelling west to east enters a chamber having a uniform electrostatic field in north to south direction. Specify the direction in which a uniform magnetic field should be set up to prevent the electron from deflecting from its straight line path.
In SI system, permeability has the units ______.
Lorentz Force generally refers to ______.
A deuteron of kinetic energy 50 keV is describing a circular orbit of radius 0.5 metre in a plane perpendicular to the magnetic field B. The kinetic energy of the proton that describes a circular orbit of radius 0.5 metre in the same plane with the same B is ______.
Show that a force that does no work must be a velocity dependent force.
A charged particle of charge e and mass m is moving in an electric field E and magnetic field B. Construct dimensionless quantities and quantities of dimension [T]–1.
An electron enters with a velocity v = v0i into a cubical region (faces parallel to coordinate planes) in which there are uniform electric and magnetic fields. The orbit of the electron is found to spiral down inside the cube in plane parallel to the x-y plane. Suggest a configuration of fields E and B that can lead to it.
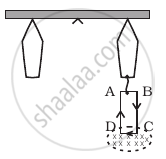
A 100 turn rectangular coil ABCD (in XY plane) is hung from one arm of a balance (Figure). A mass 500 g is added to the other arm to balance the weight of the coil. A current 4.9 A passes through the coil and a constant magnetic field of 0.2 T acting inward (in xz plane) is switched on such that only arm CD of length 1 cm lies in the field. How much additional mass ‘m’ must be added to regain the balance?
The unit Wbm-2 is equal to ______.
