Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Each of the batteries shown in figure has an emf equal to 5 V. Show that the magnetic field B at the point P is zero for any set of values of the resistances.
उत्तर
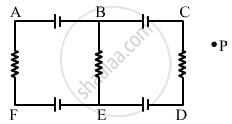
By appluing Kirchoff voltagee law,we can see that the current in the circuit is zero.
Net current in the circuit = 0
As
magnetic field is always proportional to the current flowing in the circuit hence,
Net magnetic field at point P = 0
Field at point P is independent of the values of the resistances in the circuit.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Use this law to find magnetic field due to straight infinite current carrying wire.
Deduce the expression for the magnetic field at a point on the axis of a current carrying circular loop of radius ‘R’ distant ‘x’ from the centre. Hence, write the magnetic field at the centre of a loop.
Obtain an expression for magnetic flux density B at the centre of a circular coil of radius R, having N turns and carrying a current I
Define magnetic lines of force
Define one tesla using the expression for the magnetic force acting on a particle of charge q moving with velocity \[\vec{v}\] in a magnetic field \[\vec{B}\] .
A steady current (I1) flows through a long straight wire. Another wire carrying steady current (I2) in the same direction is kept close and parallel to the first wire. Show with the help of a diagram how the magnetic field due to the current I1 exerts a magnetic force on the second wire. Write the expression for this force.
The net charge in a current-carrying wire is zero. Then, why does a magnetic field exert a force on it?
A straight wire carrying an electric current is placed along the axis of a uniformly charged ring. Will there be a magnetic force on the wire if the ring starts rotating about the wire? If yes, in which direction?
What is Lorentz force?
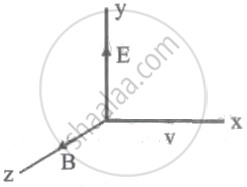
A particle with charge q moves with a velocity v in a direction perpendicular to the directions of uniform electric and magnetic fields, E and B respectively, which are mutually perpendicular to each other. Which one of the following gives the condition for which the particle moves undeflected in its original trajectory?
An electron emitted by a heated cathode and accelerated through a potential difference of 2.0 kV, enters a region with uniform magnetic field of 0.15 T. Determine the trajectory of the electron if the field (a) is transverse to its initial velocity, (b) makes an angle of 30° with the initial velocity.
The correct plot of the magnitude of magnetic field `vec"B"` vs distance r from centre of the wire is, if the radius of wire is R.
What is the magnetic induction of the field at the point O in a current I carrying wire that has the shape shown in the figure? The radius of the curved part of the wire is R, the linear parts are assumed to be very long.

Consider a wire carrying a steady current, I placed in a uniform magnetic field B perpendicular to its length. Consider the charges inside the wire. It is known that magnetic forces do no work. This implies that ______.
- motion of charges inside the conductor is unaffected by B since they do not absorb energy.
- some charges inside the wire move to the surface as a result of B.
- if the wire moves under the influence of B, no work is done by the force.
- if the wire moves under the influence of B, no work is done by the magnetic force on the ions, assumed fixed within the wire.
A cubical region of space is filled with some uniform electric and magnetic fields. An electron enters the cube across one of its faces with velocity v and a positron enters via opposite face with velocity – v. At this instant ______.
- the electric forces on both the particles cause identical accelerations.
- the magnetic forces on both the particles cause equal accelerations.
- both particles gain or loose energy at the same rate.
- the motion of the centre of mass (CM) is determined by B alone.
A 100 turn rectangular coil ABCD (in XY plane) is hung from one arm of a balance (Figure). A mass 500 g is added to the other arm to balance the weight of the coil. A current 4.9 A passes through the coil and a constant magnetic field of 0.2 T acting inward (in xz plane) is switched on such that only arm CD of length 1 cm lies in the field. How much additional mass ‘m’ must be added to regain the balance?
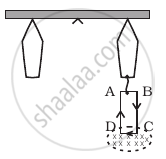
Figure shows a square loop. 20 cm on each side in the x-y plane with its centre at the origin. The loop carries a current of 7 A. Above it at y = 0, z = 12 cm is an infinitely long wire parallel to the x axis carrying a current of 10 A. The net force on the loop is ______ × 10-4 N.
A unit vector is represented as `(0.8hat"i" + "b"hat"j" + 0.4hat"k")`. Hence the value of 'b' must be ______.
State the expression for the Lorentz force on a charge due to an electric field as well as a magnetic field. Hence discuss the magnetic force on a charged particle which is (i) moving parallel to the magnetic field and (ii) stationary.
Lorentz force in vector form is ______.
