Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What is Lorentz force?
उत्तर
When a charged particle moves through a region in which both electric and magnetic fields are present, then the net force experienced by that charged particle is the sum of electrostatic force and magnetic force and is called the Lorentz force.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Two long, straight, parallel conductors carry steady currents, I1 and I2, separated by a distance d. If the currents are flowing in the same direction, show how the magnetic field set up in one produces an attractive force on the other? Obtain the expression for this force. Hence, define one ampere.
Magnetic lines of force always cross each other
Define one tesla using the expression for the magnetic force acting on a particle of charge q moving with velocity \[\vec{v}\] in a magnetic field \[\vec{B}\] .
A steady current (I1) flows through a long straight wire. Another wire carrying steady current (I2) in the same direction is kept close and parallel to the first wire. Show with the help of a diagram how the magnetic field due to the current I1 exerts a magnetic force on the second wire. Write the expression for this force.
Which of the following particles will experience maximum magnetic force (magnitude) when projected with the same velocity perpendicular to a magnetic field?
A straight wire carrying an electric current is placed along the axis of a uniformly charged ring. Will there be a magnetic force on the wire if the ring starts rotating about the wire? If yes, in which direction?
A charged particle is moved along a magnetic field line. The magnetic force on the particle is
Write the expression for the Lorentz force F in vector form.
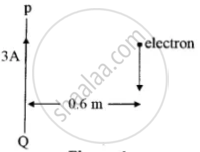
PQ is a long straight conductor carrying a current of 3A as shown in Figure below. An electron moves with a velocity of 2 x 107 ms-1 parallel to it. Find the force acting on the electron.
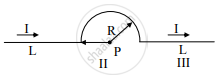
A conductor has three segments; two straights of length L and a semicircular with radius R. It carries a current I What is the magnetic field B at point P?
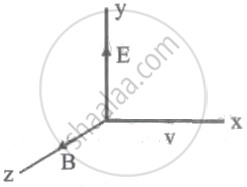
A particle with charge q moves with a velocity v in a direction perpendicular to the directions of uniform electric and magnetic fields, E and B respectively, which are mutually perpendicular to each other. Which one of the following gives the condition for which the particle moves undeflected in its original trajectory?
A charged particle is released from rest in a region of steady and uniform electric and magnetic fields which are parallel to each other. The particle will move in a ____________.
A proton enters into a magnetic field of induction 1.732 T, with a velocity of 107 m/s at an angle 60° to the field. The force acting on the proton is e = 1.6 × 10-19 C, sin 60° = cos 30° = `sqrt3/2`
A very high magnetic field is applied to a stationary charge. Then the charge experiences ______.
Direction of magnetic force on a positive charge moving in a magnetic field is given by ______.
The correct plot of the magnitude of magnetic field `vec"B"` vs distance r from centre of the wire is, if the radius of wire is R.
Which one of the following is a correct statement about magnetic forces?
A charged particle would continue to move with a constant velocity in a region wherein ______.
- E = 0, B ≠ 0.
- E ≠ 0, B ≠ 0.
- E ≠ 0, B = 0.
- E = 0, B = 0.
A charged particle of charge e and mass m is moving in an electric field E and magnetic field B. Construct dimensionless quantities and quantities of dimension [T]–1.
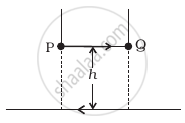
A long straight wire carrying current of 25 A rests on a table as shown in figure. Another wire PQ of length 1 m, mass 2.5 g carries the same current but in the opposite direction. The wire PQ is free to slide up and down. To what height will PQ rise?
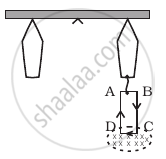
A 100 turn rectangular coil ABCD (in XY plane) is hung from one arm of a balance (Figure). A mass 500 g is added to the other arm to balance the weight of the coil. A current 4.9 A passes through the coil and a constant magnetic field of 0.2 T acting inward (in xz plane) is switched on such that only arm CD of length 1 cm lies in the field. How much additional mass ‘m’ must be added to regain the balance?
At a certain place the angle of dip is 30° and the horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field is 0.5 G. The earth’s total magnetic field (in G), at that certain place, is ______.
A long straight conductor kept along X' X axis, carries a steady current I along the +x direction. At an instant t, a particle of mass m and charge q at point (x, y) moves with a velocity `vecv` along +y direction. Find the magnitude and direction of the force on the particle due to the conductor.
With a neat labelled diagram, explain cyclotron motion and cyclotron formula.
