Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A charged particle is moved along a magnetic field line. The magnetic force on the particle is
पर्याय
along its velocity
opposite to its velocity
perpendicular to its velocity
zero
उत्तर
zero
The force on a charged particle q moving with velocity v in a magnetic field B is given by
\[( \vec{v} \times \vec{B} ) = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow \vec{F} = 0\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A horizontal overhead power line carries a current of 90 A in east to west direction. What is the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field due to the current 1.5 m below the line?
Magnetic lines of force always cross each other
A steady current (I1) flows through a long straight wire. Another wire carrying steady current (I2) in the same direction is kept close and parallel to the first wire. Show with the help of a diagram how the magnetic field due to the current I1 exerts a magnetic force on the second wire. Write the expression for this force.
A straight wire carrying an electric current is placed along the axis of a uniformly charged ring. Will there be a magnetic force on the wire if the ring starts rotating about the wire? If yes, in which direction?
Explain "Magnetic force never does any work on moving charges".
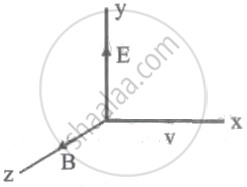
A particle with charge q moves with a velocity v in a direction perpendicular to the directions of uniform electric and magnetic fields, E and B respectively, which are mutually perpendicular to each other. Which one of the following gives the condition for which the particle moves undeflected in its original trajectory?
A proton enters into a magnetic field of induction 1.732 T, with a velocity of 107 m/s at an angle 60° to the field. The force acting on the proton is e = 1.6 × 10-19 C, sin 60° = cos 30° = `sqrt3/2`
A particle of charge -16 x 10-18 C moving with velocity 10 m/s along the X-axis enters a region where a magnetic field of induction B is along Y-axis and electric field of magnitude 104 V/m is along the negative Z-axis. If the charged particle continues moving along the X-axis, the magnitude of B is ____________.
A very high magnetic field is applied to a stationary charge. Then the charge experiences ______.
The magnetic moment is NOT associated with ____________.
An electron emitted by a heated cathode and accelerated through a potential difference of 2.0 kV, enters a region with uniform magnetic field of 0.15 T. Determine the trajectory of the electron if the field (a) is transverse to its initial velocity, (b) makes an angle of 30° with the initial velocity.
Direction of magnetic force on a positive charge moving in a magnetic field is given by ______.
- If v is parallel to B, then path of particle is spiral.
- If v is perpendicular to B, then path of particle is a circle.
- If v has a component along B, then path of particle is helical.
- If v is along B, then path of particle is a circle.
- perpendicular to direction of velocity of charged particle.
-
perpendicular to direction of magnetic field.
-
parallel to direction of velocity of charged particle.
-
parallel to the direction of magnetic field.
What is the magnetic induction of the field at the point O in a current I carrying wire that has the shape shown in the figure? The radius of the curved part of the wire is R, the linear parts are assumed to be very long.

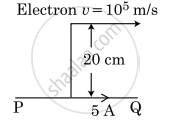
An infinitely long straight conductor carries a current of 5 A as shown. An electron is moving with a speed of 105 m/s parallel to the conductor. The perpendicular distance between the electron and the conductor is 20 cm at an instant. Calculate the magnitude of the force experienced by the electron at that instant.
A circular current loop of magnetic moment M is in an arbitrary orientation in an external magnetic field B. The work done to rotate the loop by 30° about an axis perpendicular to its plane is ______.
At a certain place the angle of dip is 30° and the horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field is 0.5 G. The earth’s total magnetic field (in G), at that certain place, is ______.
Figure shows a square loop. 20 cm on each side in the x-y plane with its centre at the origin. The loop carries a current of 7 A. Above it at y = 0, z = 12 cm is an infinitely long wire parallel to the x axis carrying a current of 10 A. The net force on the loop is ______ × 10-4 N.
Two long parallel current-carrying conductors are 0.4 m apart in air and carry currents 5 A and 10 A. Calculate the force per metre on each conductor, if the currents are (a) in the same direction and (b) in the opposite direction.
