Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An electron emitted by a heated cathode and accelerated through a potential difference of 2.0 kV, enters a region with uniform magnetic field of 0.15 T. Determine the trajectory of the electron if the field (a) is transverse to its initial velocity, (b) makes an angle of 30° with the initial velocity.
उत्तर
Magnetic field strength, B = 0.15 T
Charge on the electron, e = 1.6 × 10−19 C
Mass of the electron, m = 9.1 × 10−31 kg
Potential difference, V = 2.0 kV = 2 × 103 V
Thus, kinetic energy of the electron = eV
eV = `1/2"mv"^2`
v = `sqrt((2"eV")/"m")` .........(1)
Where,
v = velocity of the electron
(a) Magnetic force on the electron provides the required centripetal force of the electron. Hence, the electron traces a circular path of radius r.
Magnetic force on the electron is given by the relation,
Centripetal force = `"mv"^2/"r"`
∴ Bev = `"mv"^2/"r"`
r = `"mv"/"Be"` .............(2)
From equations (1) and (2), we get
r = `"m"/"Be" [(2"eV")/"m"]^(1/2)`
= `(9.1 xx 10^-31)/(0.15 xx 1.6 xx 10^-19) xx ((2 xx 1.6 xx 10^-19 xx 2 xx 10^3)/(9.1 xx 10^-31))^(1/2)`
= 100.55 × 10−5
= 1.01 × 10−3 m
= 1 mm
Hence, the electron has a circular trajectory of a radius of 1.0 mm normal to the magnetic field.
(b) When the field makes an angle θ of 30° with an initial velocity, the initial velocity will be,
v1 = v sin θ
From equation (2), we can write the expression for the new radius as:
r1 = `("mv"_1)/("Be")`
= `("mv" sin θ)/"Be"`
= `(9.1 xx 10^-31)/(0.15 xx 1.6 xx 10^-19) xx [(2 xx 1.6 xx 10^-19 xx 2 xx 10^3)/(9 xx 10^-31)]^(1/2) xx sin 30°`
= 0.5 × 10−3 m
= 0.5 mm
Hence, the electron has a helical trajectory of radius 0.5 mm along the magnetic field direction.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State whether the following statement is true or false:
Magnetic poles exist in pairs.
A charged particle is in motion having initial velocity `vecv` when it enters into a region of uniform magnetic field perpendicular to `vecv`. Because of the magnetic force the kinetic energy of the particle will ______.
A charged particle is released from rest in a region of steady and uniform electric and magnetic fields which are parallel to each other. The particle will move in a ____________.
If a particle of charge 1012 coulomb moving along the `hat"x" -` direction with a velocity 102 m/s experiences a force of 1 o-s newton in `hat"y" -` direction due to magnetic field, then the minimum magnetic field is ____________.
For a circular coil of radius R and N turns carrying current I, the magnitude of the magnetic field at a point on its axis at a distance x from its centre is given by,
B = `(μ_0"IR"^2"N")/(2("x"^2 + "R"^2)^(3/2))`
(a) Show that this reduces to the familiar result for field at the centre of the coil.
(b) Consider two parallel co-axial circular coils of equal radius R, and number of turns N, carrying equal currents in the same direction, and separated by a distance R. Show that the field on the axis around the mid-point between the coils is uniform over a distance that is small as compared to R, and is given by, B = `0.72 (μ_0"NI")/"R"` approximately.
[Such an arrangement to produce a nearly uniform magnetic field over a small region is known as Helmholtz coils.]
A charged particle of charge e and mass m is moving in an electric field E and magnetic field B. Construct dimensionless quantities and quantities of dimension [T]–1.
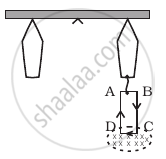
A 100 turn rectangular coil ABCD (in XY plane) is hung from one arm of a balance (Figure). A mass 500 g is added to the other arm to balance the weight of the coil. A current 4.9 A passes through the coil and a constant magnetic field of 0.2 T acting inward (in xz plane) is switched on such that only arm CD of length 1 cm lies in the field. How much additional mass ‘m’ must be added to regain the balance?
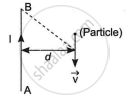
A long straight wire AB carries a current I. A particle (mass m and charge q) moves with a velocity `vec"v"`, parallel to the wire, at a distance d from it as shown in the figure. Obtain the expression for the force experienced by the particle and mention its directions.
State the expression for the Lorentz force on a charge due to an electric field as well as a magnetic field. Hence discuss the magnetic force on a charged particle which is (i) moving parallel to the magnetic field and (ii) stationary.
Two long parallel current-carrying conductors are 0.4 m apart in air and carry currents 5 A and 10 A. Calculate the force per metre on each conductor, if the currents are (a) in the same direction and (b) in the opposite direction.
