Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
An electron emitted by a heated cathode and accelerated through a potential difference of 2.0 kV, enters a region with uniform magnetic field of 0.15 T. Determine the trajectory of the electron if the field (a) is transverse to its initial velocity, (b) makes an angle of 30° with the initial velocity.
Solution
Magnetic field strength, B = 0.15 T
Charge on the electron, e = 1.6 × 10−19 C
Mass of the electron, m = 9.1 × 10−31 kg
Potential difference, V = 2.0 kV = 2 × 103 V
Thus, kinetic energy of the electron = eV
eV = `1/2"mv"^2`
v = `sqrt((2"eV")/"m")` .........(1)
Where,
v = velocity of the electron
(a) Magnetic force on the electron provides the required centripetal force of the electron. Hence, the electron traces a circular path of radius r.
Magnetic force on the electron is given by the relation,
Centripetal force = `"mv"^2/"r"`
∴ Bev = `"mv"^2/"r"`
r = `"mv"/"Be"` .............(2)
From equations (1) and (2), we get
r = `"m"/"Be" [(2"eV")/"m"]^(1/2)`
= `(9.1 xx 10^-31)/(0.15 xx 1.6 xx 10^-19) xx ((2 xx 1.6 xx 10^-19 xx 2 xx 10^3)/(9.1 xx 10^-31))^(1/2)`
= 100.55 × 10−5
= 1.01 × 10−3 m
= 1 mm
Hence, the electron has a circular trajectory of a radius of 1.0 mm normal to the magnetic field.
(b) When the field makes an angle θ of 30° with an initial velocity, the initial velocity will be,
v1 = v sin θ
From equation (2), we can write the expression for the new radius as:
r1 = `("mv"_1)/("Be")`
= `("mv" sin θ)/"Be"`
= `(9.1 xx 10^-31)/(0.15 xx 1.6 xx 10^-19) xx [(2 xx 1.6 xx 10^-19 xx 2 xx 10^3)/(9 xx 10^-31)]^(1/2) xx sin 30°`
= 0.5 × 10−3 m
= 0.5 mm
Hence, the electron has a helical trajectory of radius 0.5 mm along the magnetic field direction.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Define one tesla using the expression for the magnetic force acting on a particle of charge q moving with velocity \[\vec{v}\] in a magnetic field \[\vec{B}\] .
In SI system, permeability has the units ______.
- perpendicular to direction of velocity of charged particle.
-
perpendicular to direction of magnetic field.
-
parallel to direction of velocity of charged particle.
-
parallel to the direction of magnetic field.
The phenomenon in which a magnetic field is produced in the space near a conductor carrying current is called ______
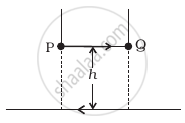
A long straight wire carrying current of 25 A rests on a table as shown in figure. Another wire PQ of length 1 m, mass 2.5 g carries the same current but in the opposite direction. The wire PQ is free to slide up and down. To what height will PQ rise?
At a certain place the angle of dip is 30° and the horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field is 0.5 G. The earth’s total magnetic field (in G), at that certain place, is ______.
An electron is moving along positive x-axis in a magnetic field which is parallel to the positive y-axis. In what direction will the magnetic force be acting on the electron?
With a neat labelled diagram, explain cyclotron motion and cyclotron formula.
