Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A long straight wire in the horizontal plane carries a current of 50 A in north to south direction. Give the magnitude and direction of B at a point 2.5 m east of the wire.
Solution
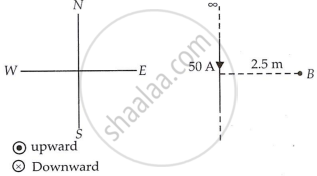
First, let's decide on the standard paper directions.
Magnitude of magnetic field,
`|vecB| = μ_0/(4pi) (2"I")/r`
= `10^-7 xx (2 xx 50)/2.5`
= 40 × 10-7 T
The direction of the magnetic field is upwards when one uses the right hand palm rule.
`vecB = 40 xx 10^-7 hatk`T
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
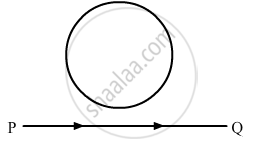
A conducting loop is held above a current carrying wire PQ as shown in the figure. Depict the direction of the current induced in the loop when the current in the wire PQ is constantly increasing.
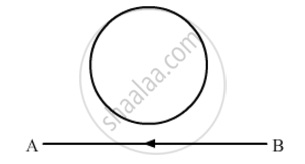
The electric current flowing in a wire in the direction from B to A is decreasing. Find out the direction of the induced current in the metallic loop kept above the wire as shown.
Explain the term hysteresis
The net charge in a current-carrying wire is zero. Then, why does a magnetic field exert a force on it?
A straight horizontal wire of mass 10 mg and length 1.0 m carries a current of 2.0 A. What minimum magnetic field B should be applied in the region, so that the magnetic force on the wire may balance its weight?
What is Lorentz force?
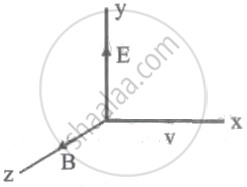
A particle with charge q moves with a velocity v in a direction perpendicular to the directions of uniform electric and magnetic fields, E and B respectively, which are mutually perpendicular to each other. Which one of the following gives the condition for which the particle moves undeflected in its original trajectory?
The magnetic moment is NOT associated with ____________.
In SI system, permeability has the units ______.
A deuteron of kinetic energy 50 keV is describing a circular orbit of radius 0.5 metre in a plane perpendicular to the magnetic field B. The kinetic energy of the proton that describes a circular orbit of radius 0.5 metre in the same plane with the same B is ______.
The magnetic moment of a current I carrying circular coil of radius r and number of turns N varies as ______.
The phenomenon in which a magnetic field is produced in the space near a conductor carrying current is called ______
In the product `vec"F" = "q" (vec"υ" xx vec"B")`
= `"q" vec"υ" xx ("B"hat"i" +"B"hat"j" + "B"_0hat"k")`
For q = 1 and `vec"υ" = 2hat"i" + 4hat"j" + 6hat"k"` and
`vec"F" = 4hat"i" - 20hat"j" + 12hat"k"`
What will be the complete expression for `vec"B"`?
A charge particle moves along circular path in a uniform magnetic field in a cyclotron. The kinetic energy of the charge particle increases to 4 times its initial value. What will be the ratio of new radius to the original radius of circular path of the charge particle:
Two conducting rails are connected to a source of emf and form an incline as shown in figure. A bar of mass 50 g slides without friction down the incline through a vertical magnetic field B. If the length of the bar is 50 cm and a current of 2.5 A is provided by battery. Value of B for which the bar slide at a constant velocity ______ × 10-1 Tesla. 2 [g = 10 m/s2]
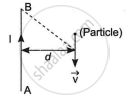
A long straight wire AB carries a current I. A particle (mass m and charge q) moves with a velocity `vec"v"`, parallel to the wire, at a distance d from it as shown in the figure. Obtain the expression for the force experienced by the particle and mention its directions.
An electron is moving along positive x-axis in a magnetic field which is parallel to the positive y-axis. In what direction will the magnetic force be acting on the electron?
Two long parallel current-carrying conductors are 0.4 m apart in air and carry currents 5 A and 10 A. Calculate the force per metre on each conductor, if the currents are (a) in the same direction and (b) in the opposite direction.
A circular coil of wire is made up of 200 turns, each of radius 10 cm. If a current of 0.5A passes through it, what will be the Magnetic field at the centre of the coil?
