Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A galvanometer of resistance 100 Ω gives a full-scale deflection for a potential difference of 200 mV.
- What must be the resistance connected to convert the galvanometer into an ammeter of the range 0-200 mA?
- Determine resistance of the ammeter.
उत्तर
(i) Given: G = 100 Ω; I = 200 mA;
Vg = 200 mV;
Resistance to be connected to the galvanometer to convert to an ammeter:
S = `("I"_"g""G")/(("I"-"I"_"g"))`
Here Ig= `("V"_"g")/"G"`
= `(200 " mV")/(100 " Ω")`
= 2 mA
S = `(2 × 10^(-3) × 100)/((0.2-0.002))`
S = 1.01 Ω
(ii) `1/"R" = 1/100 + 1/1.01`
R = 0.999 Ω
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The fraction of the total current passing through the galvanometer is ............ .
a) `S/(S+G)`
b) `G/(S+G)`
c) `(S+G)/G`
d) `(S+G)/S`
State the principle of the working of a moving coil galvanometer, giving its labeled diagram ?
What are the advantages of using soft iron as a core, instead of steel, in the coils of galvanometers?
The AC voltage across a resistance can be measured using a ______.
The deflection in a moving coil galvanometer is ______.
The coil of a moving coil galvanometer is wound over a metal frame in order to ______.
The coil of galvanometer consists of 100 turns and effective area of 1 square cm. The restoring couple is 10-8 N-m/rad. The magnetic field between the pole pieces is 5T. The current sensitivity of this galvanometer will be ______.
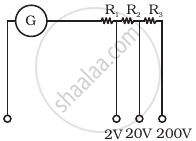
A multirange voltmeter can be constructed by using a galvanometer circuit as shown in figure. We want to construct a voltmeter that can measure 2V, 20V and 200V using a galvanometer of resistance 10Ω and that produces maximum deflection for current of 1 mA. Find R1, R2 and R3 that have to be used.
To convert a moving coil galvanometer into an ammeter we need to connect a ______.
