Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Sanya performed an experiment of obtaining characteristic curves of a junction diode. When she forward biased it, she found that beyond forward voltage V = Vk, the conductivity is very high. When she reverse biased the diode she found that a very small current (of about a few microamperes) flows in the diode. It remained constant even though she varied the voltage.
(i) In Figure 1 below, which one of the diodes is forward biased?
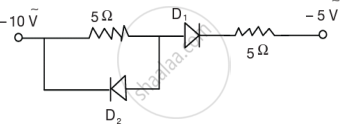
Figure 1
(ii) What is meant by a saturation current?
(iii) When applied voltage during forward bias is small, why does no current flow in the diode?
(iv) The circuit shown in Figure 2 below contains two diodes, each with a forward resistance of 50 Ω and with infinite resistance during reverse bias. If the battery voltage is 6V, then calculate the current through the 100 Ω resistance.
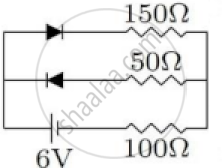
Figure 2
Solution
(i) D2 is forward biased.
(ii) It is that current which remains constant even on increasing the p.d.
(iii) Due to potential barrier or barrier p.d.
(iv) Ignoring D2 as it is reverse biased and offers infinite resistance, By Ohm's law,
`I = E/(R∗ + R∗)`
= `6/(50 + 150 + 100)`
= `6/300`
= 0.02 A
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What are α and β parameters for a transistor? Obtain a relation between them.
Write clearly, why in the case of a transistor (i) the base is thin and lightly doped
Differentiate between three segments of a transistor on the basis of their size and level of doping.
How is a transistor biased to be in active state?
When a p-n-p transistor is operated in saturation region, then its ______.
(A) base-emitter junction is forward biased and base-collector junction is reverse biased.
(B) both base-emitter and base-collector junctions are reverse biased.
(C) both base-emitter and base-collector junctions are forward biased.
(D) base-emitter junction is reverse biased and base-collector junction is forward biased
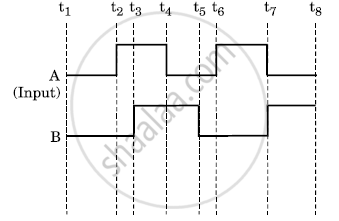
The figure shows the input waveforms A and B for ‘AND’ gate. Draw the output waveform and write the truth table for this logic gate.
Draw a typical input and output characteristics of an n-p-n transistor in CE configuration. Show how these characteristics can be used to determine (a) the input resistance (r1), and (b) current amplification factor (β)
Draw typical output characteristics of an n-p-n transistor in CE configuration. Show how these characteristics can be used to determine output resistance.
Consider the circuit arrangement shown in figure (a) for studying input and output characteristics of npn transistor in CE configuration.
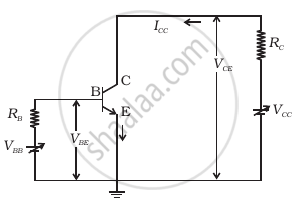 (a) |
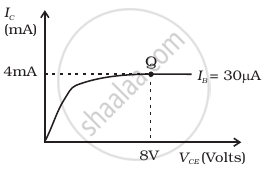 (b) |
Select the values of RB and RC for a transistor whose VBE = 0.7 V, so that the transistor is operating at point Q as shown in the characteristics shown in figure (b). Given that the input impedance of the transistor is very small and VCC = VBB = 16 V, also find the voltage gain and power gain of the circuit making appropriate assumptions.
If an emitter current is changed by 4 mA, the collector current changes by 3.5 mA. The value of β will be ______.
