Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Light
3: Sound
4: Current Electricity
5: Heat
6: Modern Physics
![Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 1 - Force, Work, Energy and Power Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 1 - Force, Work, Energy and Power - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-part-2-english-class-10-icse_6:39af211da77c495e91d1cf4305988990.PNG)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 1: Force, Work, Energy and Power
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 1 of CISCE Frank for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE.
Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 1 Force, Work, Energy and Power Exercise 1.1 i [Page 13]
Define the moment of force.
State the S.I. unit of moment of force.
Its moment of a force scalar or a vector quantity?
Name the physical quantity whose SI unit is Nm.
What is meant by a translational motion? Give one example.
What is meant by a rotatory motion? Give one example.
What is the relationship between Nm and dyne cm?
State the factors on which moment of force about a point depends.
What do you understand by the clockwise and anti clockwise moment of force?
State the condition when a force produces
(i) linear motion.
(ii) rotational motion, in a body.
Why is it easier to open a door by applying the force at the free end of it?
Why does a spanner have a long handle?
What do you mean by equilibrium of a body?
State the condition when a body is in static equilibrium.
Give one example of static equilibrium.
State the condition when a body is in dynamic equilibrium.
Give one example of dynamic equilibrium.
State two conditions for a body acted upon by several forces to be in equilibrium.
State the principle of moments.
Draw a neat labeled diagram to show the direction of two forces acting on a body to produce rotation in it. Also mark the point about which rotation takes place.
Give two examples of couple action in our daily life.
P, Q and R are three forces which act as shown in fig.
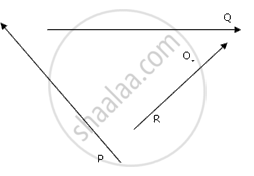
The point O lies in the same plane. Given, P = Q = R = 10N
(i) Which force has the least moment about O? Give a reason.
(ii)Which force has the greatest moment about O? Give a reason.
Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 1 Force, Work, Energy and Power Exercise 1.1 ii [Page 14]
What do you understand by the term couple?
State the couple's effect on a body.
Define the moment of a couple.
Write S.I. unit of moment of couple.
Prove that
Moment of couple = Force × couple arm.
A body is provided at a point. A force of 20 N is applied at a distance of 40 cm from the pivot. Find the moment of force about the pivot.
The moment of a force 10 N about a point 0 is 4 Nm. Calculate the distance of point of application of force from the point 0.
A mechanic can open a nut by applying a force of 200 N while using a lever handle of 50 cm length. How long handle is required if he wants to open it by applying a force of only 50 N?
State the conditions of equilibrium for a rigid body.
Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 1 Force, Work, Energy and Power Exercise 1.2 [Page 17]
What do you mean by uniform circular motion?
A uniform circular motion is an accelerated motion. Justify it.
What is a centripetal force?
Is centrifugal force considered as the force of reaction of the centripetal force?
Explain the difference between a uniform linear motion and a uniform circular motion.
Name the force needed for circular motion. What is the direction of the force?
Which of the following quantity remains constant in a uniform circular motion?
Velocity
speed
acceleration
Both velocity and speed
Is the motion of moon around the earth in circular path an accelerated motion?
Does the earth move around the sun with a uniform velocity?
What do you mean by a centrifugal force?
Name the force acting away from the centre of circular path.
Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 1 Force, Work, Energy and Power Exercise 1.3 i [Page 28]
What is the use of a fixed pulley?
What is an ideal machine?
Write the relation between mechanical advantage, velocity ratio and efficiency.
Can a machine be 100% efficient?
Define the term velocity ratio.
State the unit of velocity ratio.
What is the purpose of a machine?
Give an example for each of the following uses of a machine:
to obtain gain in force,
Give an example for each of the following uses of a machine:
to change the point of application of force
Give an example of the following uses of a machine:
to change the direction of force
Give an example of the following uses of a machine:
to obtain gain in speed
The diagram below shows a pulley arrangement.
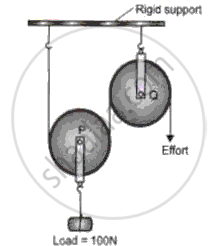
(i) In the diagram, mark the direction of the forces due to tension, acting on the pulley P.
(ii) What is the purpose of the pulley Q?
(iii) If the tension is T newton, deduce the relation between T and E.
(iv) Calculate the velocity ratio of the arrangement.
(v) Assuming that the efficiency of the system is 100%, what is the mechanical advantage?
(vi) Calculate the value of E
What is a block and tackle system of pulleys?
What is a single movable pulley?
What is the mechanical advantage of a single movable pulley in the ideal case?
Name the type of single pulley that can act as a force multiplier. Draw a labeled diagram of the pulley mentioned by you.
Give a reason for the following:
In a single fixed pulley, the velocity ratio is always more than the mechanical advantage.
Give reason for the following:
The efficiency of a pulley is always less than 100%
Give reason for the following:
In case of a block and tackle system, the mechanical advantage increases with the increase in the number of pulleys.
Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 1 Force, Work, Energy and Power Exercise 1.3 ii [Page 29]
Name a machine which is used to multiply force.
Name a machine which is used to multiply speed.
Name a machine which is used to:
change the direction of force applied.
Write two uses of pulleys. Is pulley a force multiplier?
In the fig draw a tackle to lit a load by applying the torce in a convinient direction. Mark the position of load and effort.

(i) If the load is raised by 1 m, Through what distance will the effort move?
(ii) State how many strands of tackle are supporting the load?
(iii) What is the mechanical advantage of the sysytem?
Fig shown a block and tackles system of pulleys used to lift a load.

(i) How many strands of tackle are supporting the load?
(ii) Draw arrows to represent tension in each stand.
(iii) What is the mechanical advantage of the system?
(iv) When load is pulled up by a distance 1 m how far does the effort end move?
What is a block and tackle system of pulleys?
Fig show a system of four pulleys. The upper two pulleys are fixed and the lower two are movable.
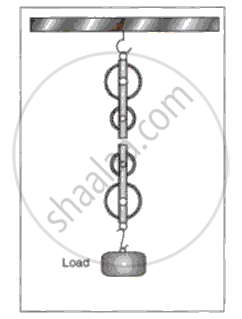
(i) Draw a string around the pulleys. Also show the place and direction in which the effort is applied.
(ii) What is the velocity ratio of the system?
(iii) What is the mechanical advantage of the system?
(iv) What assumption do you make in arriving at your answer in part (iii)?
Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 1 Force, Work, Energy and Power Exercise 1.4 i [Page 37]
Work is the application of a ....... through a distance.
A boy does work when he pushes against a brick wall. (yes/no).
What is the SI unit of work?
Nm is the unit of .......
One joule is the amount of work done when a force of ......... moves a body through a distance of .......
What is the work done when no net force is applied on the body?
Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 1 Force, Work, Energy and Power Exercise 1.4 ii [Page 38]
What is the work done when the object acted upon by a force remains at rest?
What is the work done when the force on the object and the displacement of the object are perpendicular to each other?
Is work done a scalar or a vector physical quantity?
Work is a scalar quantity because it is a measure of transfer of energy without indicating any direction
A man lifts a mass of 10 kg from the floor to a shelf 4 meter high. If g = 10 ms-2, what is the work done?
What is the work done against gravity when a body is moved horizontally along a frictionless surface?
When you move upstairs, do you perform some work?
In which one of the following cases is the work done more? When the angle between the direction of motion and that of the force is (i) 90° (ii) 0°.
A man carrying a suitcase in his hand is walking horizontally. What is the work done against gravity?
What do you mean by a kilo joule?
How many joules are there in 1 mega joule?
Define 'joule'.
What is the ratio of SI units to CGS units of 'work'?
An engine does 54,000 J of work by exerting a force of 6000 N on it. What is the displacement in the direction of the force?
How much force is applied on a body when 150 J of work is done in displacing the body through a distance of 10 m in the direction of the force?
Work done by a force is equal to the product of ....... and ....
Give two examples of work done.
On what factors does the work done by a force depend?
Write an expression for work done by a force depends?
Write an expression for the work done against gravity.
No work is done by a man moving on a horizontal road while carrying a box on his head. Explain.
Is power a scalar quantity?
Can every force produce work?
Distinguish between work and power.
Complete the following sentences:
The SI unit of work is ....... and of power is .......
Complete the following sentences:
Kilowatt is the unit of ....... and kWh is the unit of
Complete the following sentences:
Joule is the unit of .......
Complete the following sentences:
1 J = ........ Erg.
Complete the following sentences:
1 H.P. = ........ W.
A weight lifted a load of 200 kgf to a height of 2.5 m in 5 s. calculate: (i) the work done, and (ii) the power developed by him. Take g= 10 N kg-1.
Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 1 Force, Work, Energy and Power Exercise 1.4 iii [Page 39]
A boy of mass m climbs up a staircase of vertical height h.
- What is the work done by the boy against the force of gravity?
- What would have been the work done if he uses a lift in climbing the same vertical height?
Can work done be zero even if force acts on the body?
A machine raises a load of 750 N through a height of 16 m in 5s. calculate:
(i) work done by machine,
(ii) power at which the machine works.
Name the physical quantity whose MKS units are kgm2s-3.
Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 1 Force, Work, Energy and Power Exercise 1.5 i [Page 53]
State the S.I. unit of energy.
Name the type of energy possessed by a
(i) stretched catapult (ii) hot iron
(iii) wound up clock
An object is dropped from a height H. when is its
(i) P.E. maximum,
(ii) K.E. maximum,
(iii) P.E. = K.E.?
A cricket ball is thrown up from the earth's surface. What happens to its P.E.
(a) during the motion
(b) at the highest point?
Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 1 Force, Work, Energy and Power Exercise 1.5 ii [Page 54]
Name the energy changes for the following:
electric ball
Name the energy changes for the following:
bicycle brakes
Name the energy changes for the following:
pendulum
Name the energy changes for the following
human body
Name the energy changes for each of the following cases:
dynamo
A body does 20 J of work in 10 s. What is its power?
Name the physical quantity associated with the 'rate of doing work'.
An electric motor drives a machine which lifts a mass of 4 kg through a height of 10 m in 5 s at a constant speed. Assuming g = 10 ms-2, calculate
(i) the amount of work done, (ii) the power of the machine.
A 100 W electric lamp emits energy in the form of light at the rate 10 J per second. What percentage of electric energy does the lamp transform into light energy?
If an electric bulb of 100 watt is lighted for 2 hours, how much electric energy would be consumed?
A woman pulls a bucket of water of total mass 5 kg from a well which is 10 s. calculate the power used by her.
Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 1 Force, Work, Energy and Power Exercise 1 [Page 56]
What is the difference between mass and weight?
Following Fig shows piece of cardboard of uniform thickness cut into different shapes. Draw two lines to indicate the position of centre of gravity G.

Following Fig shows piece of cardboard of uniform thickness cut into different shapes. Draw two lines to indicate the position of centre of gravity G.
Following Fig shows piece of cardboard of uniform thickness cut into different shapes. Draw two lines to indicate the position of centre of gravity G.
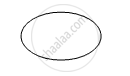
Following Fig shows piece of cardboard of uniform thickness cut into different shapes. Draw two lines to indicate the position of centre of gravity G.
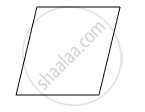
Following Fig shows piece of cardboard of uniform thickness cut into different shapes. Draw two lines to indicate the position of centre of gravity G.

Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 1 Force, Work, Energy and Power Exercise 2 [Page 57]
A body is acted upon by two forces of magnitude F but in opposite directions. State the effect of the force if both forces act at the same point of the body.
A body is acted upon by two forces of magnitude F, but in opposite directions. State the effect of the force if the two forces act at two different points of the body at a separation r.
A wheel of diameter 3 m is shown in fig. 2 with axle at 0. A force F = 8 N is applied at Q in the direction shown in figure. Calculate the moment of force about:
(i) centre o, and
(ii) point p.

Calculate the resultant moment of forces about O and state its direction in fig.
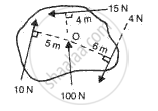
State the principle of moments. A meter scale is pivoted at 30 cm mark and it is in equilibrium when a mass of 40 g is suspended from 10 cm mark. Calculate the mass of the ruler.
State the principle of moments. A meter scale is pivoted at 30 cm mark and it is in equilibrium when a mass of 40 g is suspended from 10 cm mark. Calculate the mass of the ruler.
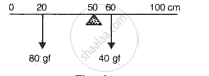
Fig. 5 shows a uniform meter scale weighing 200 gf. Provided at its centre. Two weights 300 gf and 500 gf are suspended from the ruler as shown in the diagram. Calculate the resultant torque of the ruler and hence calculate the distance from mid-point where a 100 gf should be suspended to balance the meter scale.

A meter scale is pivoted at its mid point and a 50 g mass suspended from the 20 cm mark. What mass balances the ruler when suspended from 65 cm mark?
What do you mean by the state of equilibrium? What are the conditions for stable equilibrium?
Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 1 Force, Work, Energy and Power Exercise 3 [Page 58]
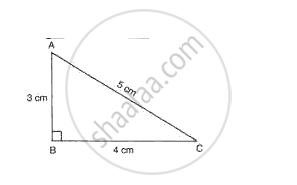
Fig. shows the dimensions of an acute angled triangle. By geometrical construction mark the C.G. of the triangle.
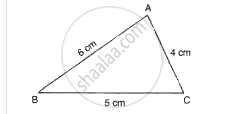
A right-angled triangle cardboard piece is placed as shown in fig. 7. Redraw the diagram showing the relative position of the vertices of the triangle when it is suspended by a pin from the hole A. Explain why the position changes?
Give scientific reason for the following:
It is easier to push a boy standing on one leg than on both legs.
Give scientific reason for the following:
When a man climbs a slope he bends forward.
Give scientific reason for the following:
There are chances of toppling when a truck takes a sharp turn especially when it is not fully loaded
Give scientific reason for the following:
A man runs in the direction of train while getting down from a moving train.
Give scientific reason for the following:
Passengers in a bus are pushed backward when it starts suddenly.
(i) What do you understand by the term couple of forces?
(ii) Calculate the moment of a couple shown in fig.
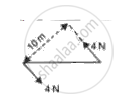
Even though the Tower of Pisa is leaning through an angle it does not fall.
Give scientific reason for the following:
While climbing a hill you will try to bend your body forward.
Give scientific reason for the following:
In a moving bus the standing passenger stands keeping both his legs apart.
Give scientific reason for the following:
In a doubled decker bus passengers are not allowed to stand in the upper deck.
Three forces A, B and C are acting on a rigid body which can turn about O in fig.9. If all the three forces are applied simultaneously, in which direction will the body move? Explain.
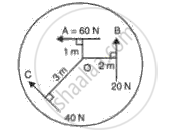
Fig. shows a uniform meter scale weighing 100 N pivoted at its centre. Two weights of 500 N and 300 N are hung from the ruler as shown in fig.
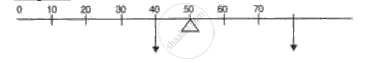
(i) Calculate total clockwise and anticlockwise moments.
(ii) Calculate difference in clockwise moment and anticlockwise moment.
(iii) Calculate the distance from O where a 100 N weight should be suspended to balance the meter scale.
A meter scale is provided at 10 cm mark and is balanced by suspending 400 g from 0 cm mark (fig. ). Calculate the mass of meter scale.

Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 1 Force, Work, Energy and Power Exercise 4 [Page 59]
Define the term work. Name the CGS and SI unit of work.
The following are some of the energy transformations.
A. Electrical to light
B. Work to heat
C. Chemical to light
D. Electrical to sound
E. Mechanical to electrical
Identify the energy transformation that takes place in the following by inserting the corresponding letter in the shape provided.
(i) A candle flame
(ii) A torch is lighted
(iii) A microphone is used in a meeting
(iv) A cycle dynamo
(v) A piece of metal is being filed
A boy pulls a box up to 10 m with a force of 5 kgf. Calculate the work done by him.
Calculate the amount of work done by a child carrying a bag of 20 kg when he moves a distance of 40 m in
(a) Vertical direction, and
(b) Horizontal direction
(a) Define power and name its unit.
(b) A girl weighting 50 kg climbs up 60 steps each of 20 cm height in 5 minutes. Calculate the power developed.
When an elevator starts to move down suddenly we experience 'weightlessness'. Explain.
A block of mass 20 kg is pulled up a slope (fig.12) with a constant speed by applying a force of 500 N parallel to the slope. A and B are initial and final positions of the block.
(a) Calculate the work done by the force in moving the block from A and B.
(b) Calculate the potential energy gained by the block.
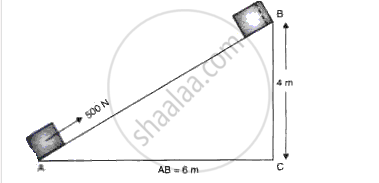
How fast should a boy weighting 30 kg run so that his kinetic energy is 375 joule?
A girl of mass 50 kg runs up a flight of 40 steps in 20 seconds. If each step in 20 cm high, calculate the power developed by the girl. (g= 10 ms-2).
Define energy and state the unit of energy and the law of conservation of energy.
List any six forms of energy and write a short note on each of them.
What do you understand by 'potential energy' and 'Kinetic energy'? Give three examples of each to illustrate your answer.
A bullet is of mass 'm' g and is moving with a velocity 'v' m/s. Find the kinetic energy of the bullet when
(a) The mass is doubled,
(b) The velocity is tripled.
Identify the type of energy possessed by the body in each of the following:
(a) A coiled spring of the toy car
(b) A hammer which is raised
(c) A stone shot from a catapult
(d) Water stored in the overhead tank
(e) A tadpole moving in water.
Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 1 Force, Work, Energy and Power Exercise 5 [Page 60]
Fill in the boxe to show the corresponding energy transformation.

Fill in the boxe to show the corresponding energy transformation.
Fill in the boxe to show the corresponding energy transformation.

Fill in the boxe to show the corresponding energy transformation.

Fill in the boxe to show the corresponding energy transformation.

State the energy changes which take place when Water stored in the dam is used to turn turbine in dynamo.
State the energy changes which take place when An electric bulb glows when it is connected to a source of electric current.
State the energy changes which take place when A piece of magnesium wire is burnt in a jar of oxygen.
State the energy changes which take place when A stone dropped from the top of a cliff reaches the ground after some time.
State the energy changes which take place when A toy car with a wound spring moves on ground.
Give an example
Electrical energy changes of sound energy.
Give an example
Chemical energy changes to heat energy.
Give an example
Chemical energy changes to electrical energy.
Give an example
Light energy changes to electrical energy.
Give an example
Electrical energy changes to heat energy.
Define Simple machine
Define Lever
Define Mechanical advantage
Define Velocity Ratio
Define Efficiency
Class I lever can have M.A. = 1, M.A. < 1 and M.A. > 1. Explain each giving examples.
Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 1 Force, Work, Energy and Power Exercise 6 [Page 61]
Fig. shows a spade. It is being used to lift soil weighing 30N from the ground.
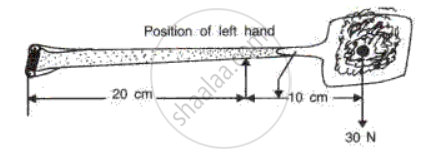
(a) Mark the direction of the least force on the handle necessary to keep the spade balanced.
(b) Calculate the least force on the handle necessary to keep the spade balanced (the weight of the spade is negligible).
(c) If the left hand was move towards the soil on the spade, would the force on the handle necessary to keep the soil balance the greater or less? Give a reason for your answer.
(d) To which class of lever does the spade belong?
A pair of nut crackers is 12 cm long. An effort of 10 gf is required to crack a nut which is passed at a point 3 cm from the finger. Calculate the load Fig.

(a) Fig represents an incomplete diagram of a simple string pulley system. Copy this diagram on a new page and complete it and mark where the effort must be applied to lift the load.
(b) What is the velocity ratio of this system?
(c) If the pulley system is 80% efficient and the load is 720 N, then
(i) What effort must be applied to lift the load?
(ii) What work must be done must be done in lifting the load through a distance of 2 m using this machine?
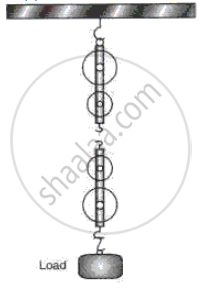
What makes a balance faulty?
A faulty balance of equal arms but pans of unequal weight is used to find the weight of a body. By the method of double weighing the weights are found as 8 kg and 8.2 kg. Find the actual weight of the body.
The arms of a beam balance are 20 cm and 21 cm, but the pans are of equal weight. By the method of double weighing the weights are found to be 1000 g and 20 g. Find the actual weight of the body
A faulty balance of unequal arms and pans of unequal weights is used to find the true weight of a metal. By double weighing the weights are found to be 1210 g and 1000 g. Calculate the true weight of the metal.
Solutions for 1: Force, Work, Energy and Power
![Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 1 - Force, Work, Energy and Power Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 1 - Force, Work, Energy and Power - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-part-2-english-class-10-icse_6:39af211da77c495e91d1cf4305988990.PNG)
Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 1 - Force, Work, Energy and Power
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Frank solutions for Mathematics Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE 1 (Force, Work, Energy and Power) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Frank textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 1 Force, Work, Energy and Power are Work Done by the Force of Gravity (W = mgh), Forms of Energy, Gravitational Potential Energy at a Height (U = mgh), Concept of Work, Measurement of Work, Power, Energy, Mechanical Energy, Potential Energy (U), Types of Potential Energy, Kinetic Energy (K), Types of Kinetic Energy, Conversion of Potential Energy into Kinetic Energy, Transformation of Energy, Principle of Conservation of Energy, Theoretical verification of K + U = Constant for a freely falling body, Application of Principle of Conservation of Energy to a Simple Pendulum, Concept of Work, Machines, Simple Machines, Machines (Numerical), A Lever, A Pulley, Principle of Machine, Relationship between efficiency (ղ), mechanical advantage (M.A.) and velocity ratio (VR), Types of Levers, Single Fixed Pulley, Technical Terms Related to a Machine, Single Movable Pulley, Combination of Pulleys, Examples of Each Class of Levers as Found in the Human Body, Force, Translational and Rotational Motions, Couple, Principle of Moments, Uniform Circular Motion (UCM), Centrifugal Forces, Centripetal Force, Moment (Turning Effect) of a Force Or Torque, Equilibrium of Bodies and Its Types, Centre of Gravity.
Using Frank Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE solutions Force, Work, Energy and Power exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Frank Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE students prefer Frank Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 1, Force, Work, Energy and Power Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE additional questions for Mathematics Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
