Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In the fig., PO is a ray of light incident on a rectangular glass block.
(a) Complete the path of the ray through the block.
(b) In the diagram, mark the angle of incidence (i) and the angle of refraction (r) at the first interface. How is the refractive index of glass related to the angles I and r?
(c) Mark angle of emergence by the letter e. How are the angles i and e related?
(d) Which two rays are parallel to each other? Name them.
(e) Indicate in the diagram the lateral displacement between the emergent ray and the incident ray.
Solution
(a) Diagram showing complete path of light :
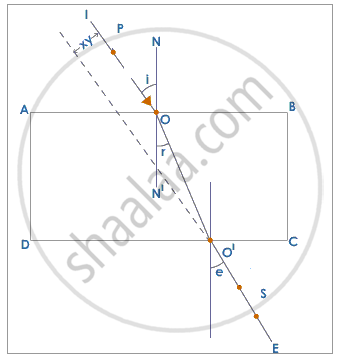
(b) Angle of incidence and angle of refraction marked in the above diagram.
R.I = `"sin i"/"sin r"`
(c) Angle of emergence is marked in the above diagram.
Angle of incidence = Angle of emergence
(d) Rays IO and O'E are parallel to each other. These are incident and emergent rays respectively.
(e) In the diagram above, the lateral displacement is indicated by XY.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain the term absolute refractive index of a medium and write an expression to relate it with the speed of light in vacuum.
Name a prism required for obtaining a spectrum of Ultraviolet light.
Which of the above wavelengths has a higher frequency?
For which colour of white light, is the refractive index of a transparent medium the most?
When a ray of light from air enters a denser medium, it ______.
Fill in the blanks to complete the following sentence
When light travels from a denser to a rarer medium, its speed ……………….
The refractive index of air with respect to glass is expressed as `""_g μ_a=sin i /sin r`.
- Write down a similar expression for aμg in terms of the angles i and r.
- If angle r = 90°, what is the corresponding angle i called?
- What is the physical significance of the angle i in part (b)?
Select from the following the best experimental set-up for tracing the path of a ray of light through a glass slab: (A) I
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
A ray of monochromatic light is incident from air into a glass slab. Draw a labelled ray diagram indicating the change in its path till it emerges out of the slab. In the diagram, mark the angle of incidence (i) and the angle of refraction (r) at the first interface. How is the refractive index of glass related to the angles i and r?
Explain with the help of a diagram of how fish is able to see the objects above it.
