Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A spherical marble, of refractive index 1.5 and curvature 1.5 cm, contains a tiny air bubble at its centre. Where will it appear when seen from outside?
Options
1 cm inside
at the centre
`5/3` cm inside
2 cm inside
Solution
`bb(5/3)` cm inside
Explanation:
The refractive index of the marble is 1.5.
One can see the image formed due to the reflection in the spheres.
In order to determine the distance where the image will form, use the lens maker formula.
Hence, `mu_1/v - mu_2/u = (mu_2 - mu_1)/"R"`
Where, refractive index of air = 1, refractive index of glass = 1.5, Radius of the curvature = 1.5 cm
Substituting the values, we get,
`therefore 1/v - 1.5/0.75 = (1 - 1.5)/1.5`
`therefore 1/v - 2 = - 0.5/1.5`
`therefore 1/v - 2 = - 1/3`
`therefore 1/v = - 1/3 + 2`
`therefore 1/v = (- 1 + 6)/3`
`therefore 1/v = 5/3`
Therefore, the tiny bubble will be seen 5/3 cm inside when we see it from the outside.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Name the factors affecting the critical angle for the pair of media.
The figure shows a ray of light falling normally on the face AB of an equilateral glass prism having refractive index`3/2`, placed in water of refractive index `4/3`.Will this ray suffer total internal reflection on striking the face AC? Justify your answer.
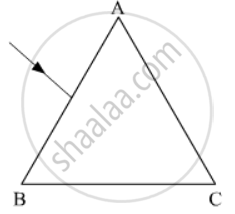
What do you understand by the deviation produced by a prism? Why is it caused?
What is total internal reflection?
State two conditions necessary for total internal reflection to occur.
In the given figure PQ and PR are the two light rays emerging from an object P. The ray PQ is refracted as QS.
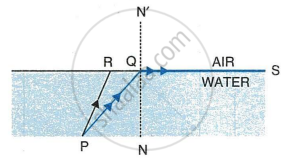
- State the special name given to the angle of incidence ∠PQN of the ray PQ.
- What is the angle of refraction for the refracted ray QS?
- Name the phenomenon that occurs if the angle of incidence ∠PQN is increased.
- The ray PR suffers partial reflection and refraction on the water-air surface. Give reason.
- Draw in the diagram the refracted ray for the incident ray PR and hence show the position of image of the object P by the letter P’ when seen vertically from above.
Plot a graph between
Angle of incidence versus angle of reflection,
In the following figure, show two rays A and B travelling from water to air. If the critical angle for water- air surface is 48°, complete the ray diagram showing the refracted rays for each. State conditions when the ray will suffer total internal reflection.

Can light be ‘piped’ like sound in a doctor’s stethoscope?
Express the refractive index μ of a medium in terms of the angle of incidence i in air and the angle of refraction r in a denser medium.
If a ray of light passes from medium I to medium II without any change of direction, what can be said about the refractive indices of these media (angle I is not 0)?
State two advantages of using a right-angle prism as a reflector, rather than a plane mirror.
What is meant by the term ‘critical angle’?
The diagram shows a point source P inside a water container. Three rays A, B, and C starting from P are shown up to the water surface. Show in the diagram the path of these rays after striking the water surface. The critical angle for the water-air pair is 48°.
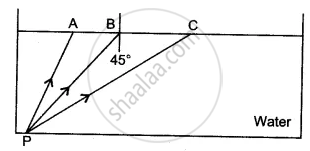
A ray of light is incident on a glass surface at an angle of 50° with the corresponding angle of refraction 30°. Find the value of the R.I. of glass.
A ray of light is incident as a normal ray on the surface of separation of two different mediums. What is the value of the angle of incidence in this case?
Answer the following question.
Under what conditions are total internal reflection possible? Explain it with a suitable example.
The resultant `vec"R"` of `vec"P"` and `vec"Q"` is perpendicular to `vec"P"`. Also `|vec"P"|=|vec"R"|`. The angle between `vec"P"` and `vec"Q"` is ______.
[tan 45° = 1]
The outer concentric shell in optic fiber is called ______.
Define the critical angle.
A green light is incident from the water to the air-water interface at the critical angle (θ). Select the correct statement.
The phenomena involved in the reflection of radiowaves by ionosphere is similar to ______.
A rectangular block of glass ABCD has a refractive index 1.6. A pin is placed midway on the face AB (Figure). When observed from the face AD, the pin shall ______.
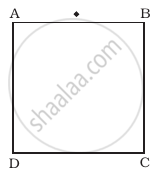
- appear to be near A.
- appear to be near D.
- appear to be at the centre of AD.
- not be seen at all.
The angle made by incident ray of light with normal of the reflecting surface is called ______.
Name any two phenomena which take place in the formation of a rainbow.
State two differences between normal reflection and total internal reflection.
