Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A spherical marble, of refractive index 1.5 and curvature 1.5 cm, contains a tiny air bubble at its centre. Where will it appear when seen from outside?
विकल्प
1 cm inside
at the centre
`5/3` cm inside
2 cm inside
उत्तर
`bb(5/3)` cm inside
Explanation:
The refractive index of the marble is 1.5.
One can see the image formed due to the reflection in the spheres.
In order to determine the distance where the image will form, use the lens maker formula.
Hence, `mu_1/v - mu_2/u = (mu_2 - mu_1)/"R"`
Where, refractive index of air = 1, refractive index of glass = 1.5, Radius of the curvature = 1.5 cm
Substituting the values, we get,
`therefore 1/v - 1.5/0.75 = (1 - 1.5)/1.5`
`therefore 1/v - 2 = - 0.5/1.5`
`therefore 1/v - 2 = - 1/3`
`therefore 1/v = - 1/3 + 2`
`therefore 1/v = (- 1 + 6)/3`
`therefore 1/v = 5/3`
Therefore, the tiny bubble will be seen 5/3 cm inside when we see it from the outside.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Which colour of light has a higher critical angle? Red light or green light.
In the given figure PQ and PR are the two light rays emerging from an object P. The ray PQ is refracted as QS.
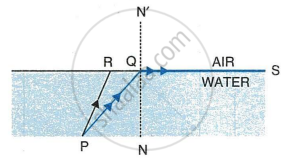
- State the special name given to the angle of incidence ∠PQN of the ray PQ.
- What is the angle of refraction for the refracted ray QS?
- Name the phenomenon that occurs if the angle of incidence ∠PQN is increased.
- The ray PR suffers partial reflection and refraction on the water-air surface. Give reason.
- Draw in the diagram the refracted ray for the incident ray PR and hence show the position of image of the object P by the letter P’ when seen vertically from above.
Write the necessary conditions for the phenomenon of total internal reflection to
occur ?
Solve the previous problem if the paperweight is inverted at its place so that the spherical surface touches the paper.
Plot a graph between
Angle of incidence versus angle of reflection,
Plot a graph between
Angle of incidence versus angle of refraction.
Name the principle on the basis of which optical fibres work.
How does a ray of light bend when it travels from rarer to denser medium
Why do diamonds sparkle?
State one factor on which a critical angle for a given pair of media depends. The critical angle for the glass-air interface is 45° for the yellow light. Will it be equal to, less than or greater than 45° for (i) red light, (ii) blue light?
The adjacent diagram shows two right-angled isosceles prisms A and B. Complete the diagram to show the path of rays P and Q emerging out of the prism B. What principles have you used to complete the diagram?
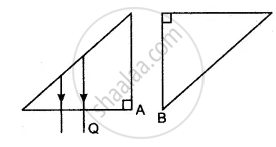
Choose the correct option.
Consider the following phenomena/ applications: P) Mirage, Q) rainbow, R) Optical fibre and S) glittering of a diamond. Total internal reflection is involved in
Answer the following question.
Explain ‘mirage’ as an illustration of refraction.
Answer the following question.
Under what conditions are total internal reflection possible? Explain it with a suitable example.
Answer the following question.
Define the critical angle of incidence and obtain an expression for it.
Answer the following question.
Describe the construction and working of an optical fibre.
The entire light is reflected back into the denser medium is called ______.
The angle of incidence at which the angle of refraction is Q£ is called the critical angle.
What is a mirage? How does it occur?
A green light is incident from the water to the air-water interface at the critical angle (θ). Select the correct statement.
The phenomena involved in the reflection of radiowaves by ionosphere is similar to ______.
A Rainbow is a beautiful natural phenomenon formed because of the following:
A ray of light passes through a prism of refractive index `sqrt2` as shown in the figure. Find:
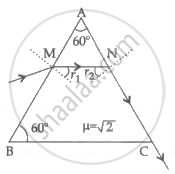
- The angle of incidence (∠r2) at face AC.
- The angle of minimum deviation for this prism.
A light is entering from one medium refractive index `("RI" =5/3)` to another medium at an angle 30°. The angle of refraction for other medium is sin-1 `(5/6)`. then the increase in angle of incidence is ______ such that the ray of light reflected back into the same medium.
The angle made by incident ray of light with normal of the reflecting surface is called ______.
An endoscope uses optic fiber to transmit high resolution images of internal organs without loss of information. The principle of light that is used by the optic fiber is based on ______.
