Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Solve the previous problem if the paperweight is inverted at its place so that the spherical surface touches the paper.
उत्तर
Given,
Taking the radius of the paperweight as its thickness = 3 cm
Refractive index of the paperweight (μg) = 3/2
Refractive index of the air (μ1) = 1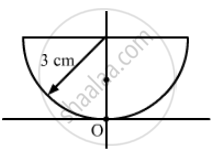
Image shift is given by:
\[∆ t = \left( 1 - \frac{1}{\mu} \right)t\]
\[ = \left( 1 - \frac{2}{3} \right)3\]
\[ = \left( \frac{1}{3} \right)3\]
\[ = 1 \text{ cm }\]
The upper surface of the paperweight is flat and the spherical spherical surface is in contact with the printed letter.
Therefore, we will take it as a simple refraction problem.
Hence, the image will appear 1 cm above point A.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
You are given prisms made of crown glass and flint glass with a wide variety of angles. Suggest a combination of prisms which will
(a) deviate a pencil of white light without much dispersion,
(b) disperse (and displace) a pencil of white light without much deviation.
Draw the diagram of a right-angled isosceles prism which is used to make an invented image erect
In the given figure PQ and PR are the two light rays emerging from an object P. The ray PQ is refracted as QS.
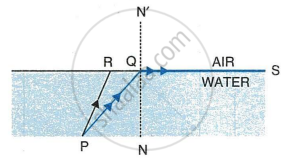
- State the special name given to the angle of incidence ∠PQN of the ray PQ.
- What is the angle of refraction for the refracted ray QS?
- Name the phenomenon that occurs if the angle of incidence ∠PQN is increased.
- The ray PR suffers partial reflection and refraction on the water-air surface. Give reason.
- Draw in the diagram the refracted ray for the incident ray PR and hence show the position of image of the object P by the letter P’ when seen vertically from above.
Write the necessary conditions for the phenomenon of total internal reflection to
occur ?
i) Observe the given figure and answer the following questions.
a) Identify and write the natural process shown in the figure.
b) List the phenomena which are observe in this process.
c) Redraw the diagram and show above phenomena in it.
State two advantages of using a right-angle prism as a reflector, rather than a plane mirror.
A ray of light incident at an angle of incidence ‘i’ passes through an equilateral glass prism such that the refracted ray inside the prism is parallel to its base and emerges from the prism at an angle of emergence ‘e’.
What can you say about the value of the angle of deviation in such a situation?
Name the factors affecting the critical angle for the pair of media.
What is meant by the term ‘critical angle’?
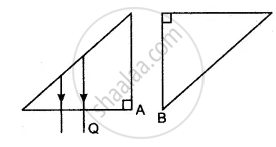
The adjacent diagram shows two right-angled isosceles prisms A and B. Complete the diagram to show the path of rays P and Q emerging out of the prism B. What principles have you used to complete the diagram?
PQ and PR are two light rays emerging from the object as shown in the figure below:
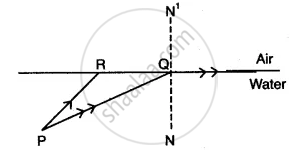
(i) What is the special name given to the angle of incidence (∠PQN) of ray PQ?
(ii) Copy the ray diagram and complete it to show the position of the image of the object P when seen obliquely from above.
(iii) Name the phenomenon that occurs if the angle of incidence ∠PQN is increased still further.
Answer the following question.
Describe the construction and working of an optical fibre.
Optical fibre communication uses the principle of ______.
Which of the following statements about total internal reflection is true?
What is a mirage? How does it occur?
What are the examples of total internal reflection in nature?
A light is entering from one medium refractive index `("RI" =5/3)` to another medium at an angle 30°. The angle of refraction for other medium is sin-1 `(5/6)`. then the increase in angle of incidence is ______ such that the ray of light reflected back into the same medium.
